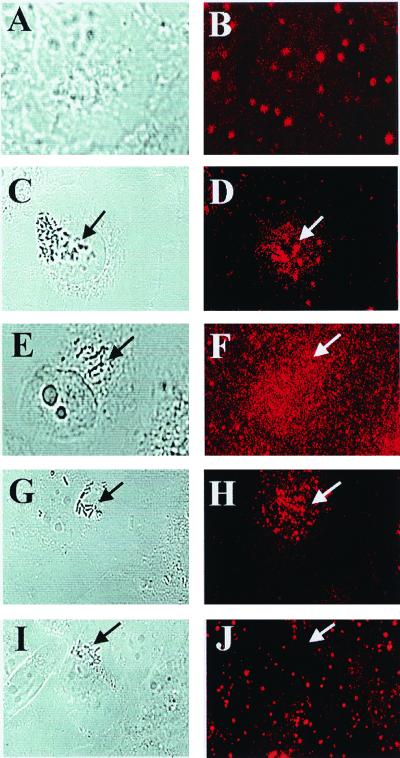
FIG. 5.
Overexpression of mutant forms of FAK inhibits the accumulation of native FAK at bacterial entry sites. HBMEC, uninfected and nontransfected, were used as controls (A and B) to show the normal pattern. HBMEC either nontransfected (C and D) or transfected with plasmids containing FRNK (E and F), Phe397 FAK (G and H), and Arg454 FAK (I and J) were treated with E44 for 15 min, fixed, and stained with anti-FAK antibody as described in Materials and Methods. Confocal laser microscopy was used to visualize the bacteria by transmitted light optics (A, C, E, G, and I) and FAK by TRITC-conjugated secondary antibody to anti-FAK antibody (B, D, F, H, and J). Arrows indicate locations of bacteria or accumulation of FAK.