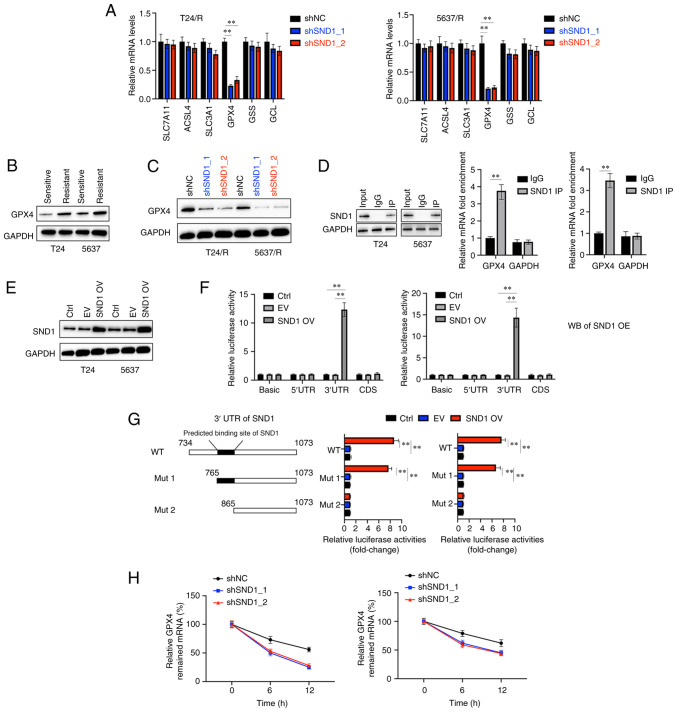
Figure 3.
SND1 directly binds to the 3′UTR of GPX4 mRNA and stabilises it. (A) T24/R and 5637/R cells were transfected as indicated, and the mRNA levels of indicated genes were determined. (B) The protein levels of GPX4 were assessed in T24, T24/R, 5637 and 5637/R cells. (C) T24/R and 5637R cells were transfected as indicated, and the protein levels of GPX4 were assessed. (D) T24/R and 5637/R cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with SND1 antibody or control IgG and GAPDH followed by immunoblotting analysis (left). Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of the relative enrichment of GPX4 mRNA in SND1-RNA binding complexes, using anti-IgG as a negative control (right). (E) T24 and 5637 cells were transfected as indicated, and the protein levels of SND1 were measured. (F) 5′UTR, 3′UTR and CDS of GPX4 were cloned into a luciferase reporter vector and co-transfected with a vector that expressed SND1 in the T24 and 5637 cells, and the relative luciferase activities were measured. (G) Wild-type or truncated 3′UTR sequences (Mut 1, Mut 2) of GPX4 3′UTR were co-transfected with SND1-expressing vector into T24 and 5637 cells, and the relative luciferase activities were measured. (H) GPX4 mRNA abundance in shNC or shSND1_1 or shSND1_2 transfected cells after actinomycin D (2.5 µg/ml) administration at different time-points (10 and 24 h). Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. **P<0.01. SND1, staphylococcal nuclease and tudor domain containing 1; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; CDS, coding sequence; sh, short hairpin RNA; NC, negative control; Ctrl, control; EV, empty vector; OV, overexpression.