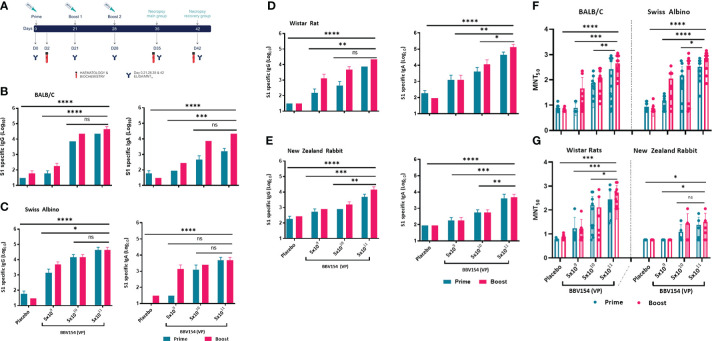
Figure 3.
Candidate vaccine BBV154 elicits robust humoral immune responses in BALB/c, Swiss albino mice, Wistar rats and New Zealand White Rabbits. Schematic diagram of repeated dose administration of BBV154 to 6–8-week-old, male and female BALB/c or Swiss albino or Wistar rats (n = 10–12) or 10–12-week-old male and female New Zealand White rabbits (n = 6–8). Animals were immunized with placebo or three different concentrations of BBV154 vaccine candidate via the intranasal route in 50 μl (mice),100 μl (rat), and 200 μl (rabbit) on day 0 and boosted on day 21 (BALB/c & Rabbits) or 22 (Swiss albino and rats), and day 28 or 29 (A). Antibody responses in sera of immunized animals at day 21 after priming or at day 28 or 29 after one-week post-boosting were evaluated (B-E). SARS-CoV-2 S1-specific IgG (left panel) and IgA (right panel) levels were measured by ELISA using pooled sera of BALB/c (B), Swiss albino (C), Wistar rats (D) and New Zealand White Rabbits (E). Neutralizing activity of immune serum against SARS-CoV-2 performed by MNT50 at day 21 after priming or at day 28 or 29 after one-week post-boosting (F-G). Data points represent mean ± SEM of individual animal data. Statistical analysis was performed with nonparametric t-test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.