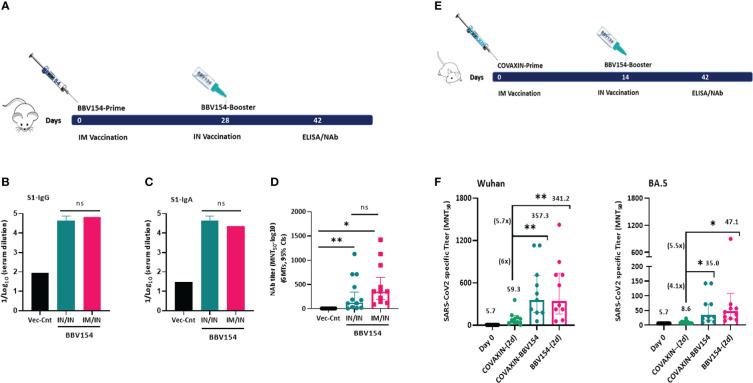
Figure 6.
Comparison of humoral immune responses induced by a systemic prime-intranasal boost strategy by homologous or heterologous COVID-19 vaccines. 5–6-week-old BALB/c male and female mice (n=10-12) were primed intranasally or intramuscularly with 5x1010 VP of Vector control or BBV154 on day 0 and boosted IN on day 28 (A). Two-weeks post-booster vaccination SARS-CoV-2 spike specific IgG (B) and IgA (C) were assessed by ELISA, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies by MNT50 (D). 6–8-week-old male and female Wistar rats (n = 10) in three groups were immunized with homologous BBV154 prime and BBV154 booster (one-fifth of a human single dose) or COVAXIN prime and COVAXIN [one-fifth of a human single dose) booster or heterologous (COVAXIN prime and BBV154 booster) regimens on day 0 and 14 (E) four-weeks post-booster vaccination neutralizing activity of immune serum (F) against SARS-CoV-2 ancestral (Wuhan) or omicron variant (BA.5) was performed by MNT50. The numbers in parentheses indicate the GMT and fold change in neutralization titer against COVAXIN homologous group compared with the heterologous (COVAXIN/BBV154) or BBV154 homologous groups. Error bars indicate mean with 95% CI. Statistical analysis was performed with nonparametric t-test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.