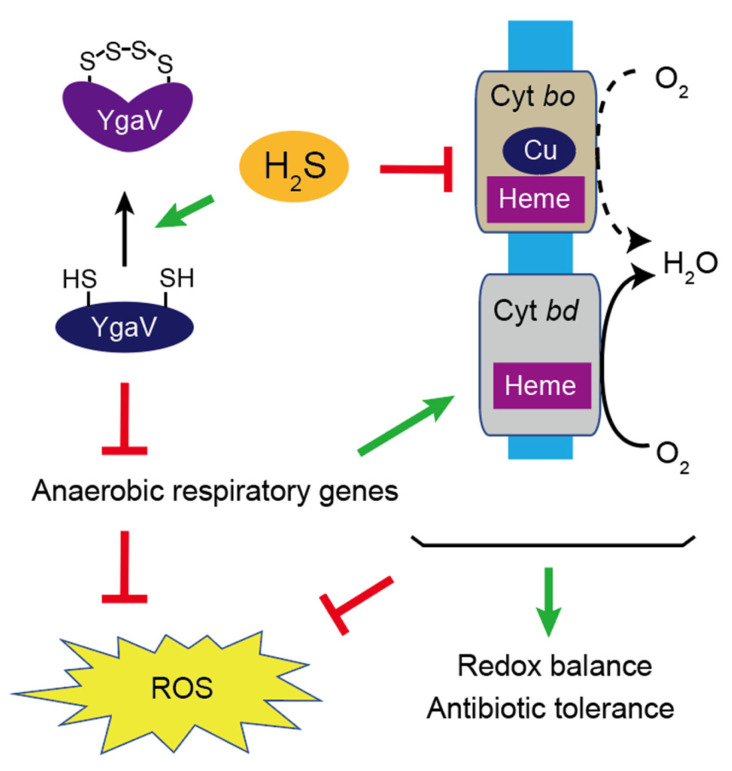
Figure 11.
A schematic model for YgaV-dependent control of gene expression and its physiological function. H2S inhibits activity of the energy-efficient cytochrome bo oxidase, which causes ROS accumulation. In the presence of H2S, two cysteine residues of YgaV form an intramolecular tetrasulfide bond to derepress anaerobic-respiratory and ROS-scavenging genes, which contributes to redox homeostasis, ROS scavenging and antibiotic tolerance.