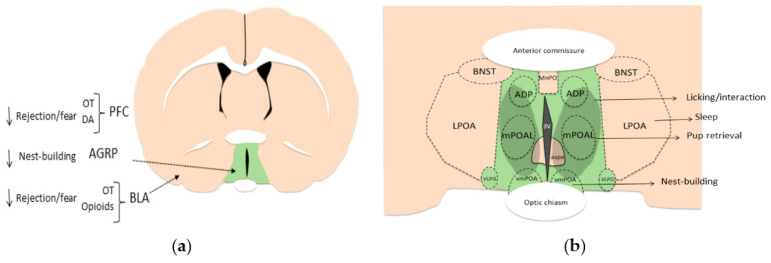
Figure 2.
(a) Coronal drawing of a rat brain (modified from [132]). The green region represents the medial preoptic area (mPOA) as the main generator of maternal motivation via oxytocin (OT) and dopamine (DA) activity. Agouti-related peptide (AGRP) facilitates rejection in mPOA, but OT, DA, and opioids reduce rejection via other regions such as prefrontal cortex (PFC, not shown) and basolateral amygdala (BLA). (b) Amplification of the mPOA and subregions in the rat brain. Darker green spot represents putative galanin/ER+ neurons that mediate the expression of licking and pup retrieval in the lateral (mPOAL) and dorsal (ADP) parts of mPOA, where OT neurons are also found (modified from [103]). Nest-building depends on the activity of the ventral portion of the mPOA (vmPOA). Also shown are the bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BNST), median preoptic nucleus (MnPO), ventrolateral nucleus (vlPO), anteroventral periventricular nucleus (avpv), and lateral preoptic area (LPOA) that mediates sleep. Different mPOA subregions mediate diverse maternal behaviors interacting with mesolimbic regions.