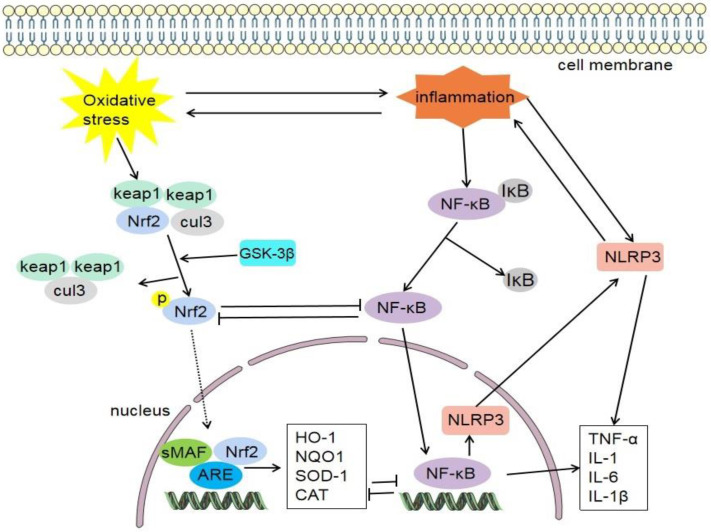
Figure 5.
NF-κB is usually associated with IκB and forms stable NF-κB/IκB complex. Inflammatory reaction promotes the dissociation of NF-κB/IκB complex and separates active NF-κB. NF-κB can promote the expression of NLRP3, and then promote the inflammatory response. NF-κB can also promote the release of inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-1β). Nrf2 can negatively regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway. Keap1, cytoplasmic kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; sMAF, small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; ARE, antioxidant response element; cul3, cullin-3; NLRP3, nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; NQO1, quinine oxidoreductase 1; SOD-1, superoxide dismutase-1; CAT, catalase; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-kappa B; IκB, inhibitor κB; IL-1β, interleukin-1 β; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor-alpha.