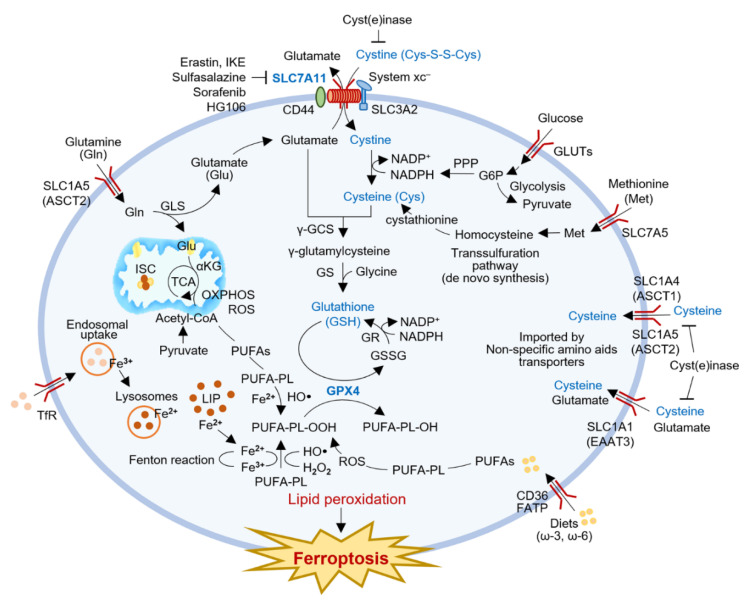
Figure 1.
Role of SLC7A11-GSH-GPX4 axis in redox signaling and ferroptosis induction. SLC7A11 is the primary transporter for cystine import combined with glutamate export. GSH is the most abundant intracellular antioxidant composed of three amino acids; glutamate, glycine, and cysteine. Cystine uptake is essential for intracellular cysteine production and GSH biosynthesis. Cysteine may also be generated partly de novo via the transsulfuration pathway through a reduction reaction consuming NADPH or other non-specific amino acid transporters. GSH is a cofactor of GPX4, contributing to the detoxification of lipid peroxides into lipid alcohols. Therefore, GSH depletion is responsible for iron-catalyzed, lipid peroxidation-dependent, non-apoptotic cell death, known as ferroptosis. The Fenton reaction is the reaction between ferrous iron and hydrogen peroxide to form hydroxyl or peroxyl radicals that react with membrane lipids and rapidly propagate to neighboring PUFA-PL. Excessively produced lipid peroxidation disrupts the integrity of cell membranes, resulting in cell death. α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; ASCT1/2, alanine-serine cysteine transporters 1 and 2; CoA, coenzyme A; γ-GCS, γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase; GLS, glutaminase; GLUTs, glucose transporters; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GR, glutathione reductase; GS, glutathione synthetase; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; HO·, hydroxyl radical; IKE, imidazole ketone erastin; ISC, iron-sulfur cluster; LIP, labile iron pool; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; PUFA-PL, polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing phospholipid; PUFA-PL-OH, polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing phospholipid alcohol; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; SCD, stearoyl-CoA desaturase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SLC7A11 (xCT), solute carrier family 7 member 11; system xc−, cystine/glutamate exchange transporter; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; Tfr, transferrin receptor.