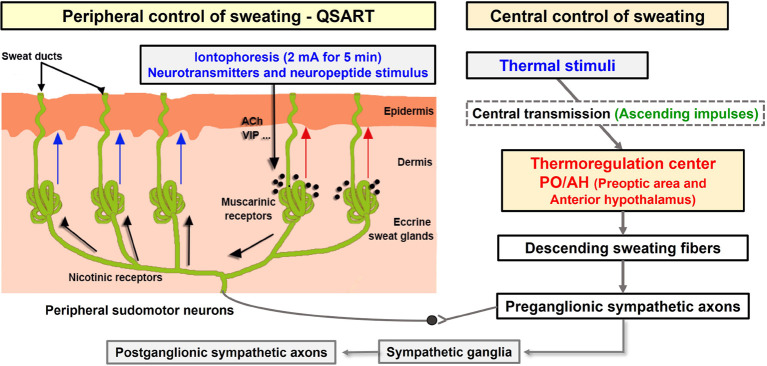
SCHEME 2.
Schematic of the sudomotor axon reflex via iontophoresis. Cholinergic agonists (such as acetylcholine) and neuropeptides (such as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide) administered via iontophoresis (shown with the black arrow) bind to muscarinic receptors causing local sweat production (direct sweat, red arrow). The cholinergic agonist simultaneously binds to nicotinic receptors on the nerve terminals of sudomotor fibers triggering an antidromic impulse. This impulse travels orthodromically to a neighboring population of eccrine sweat glands at branch points resulting in an indirect axon-mediated sweat response (indirect sweat, blue arrows) (18). Modified model by Kwon et al. ACh, acetylcholine; VIP, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. QSART, quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test.