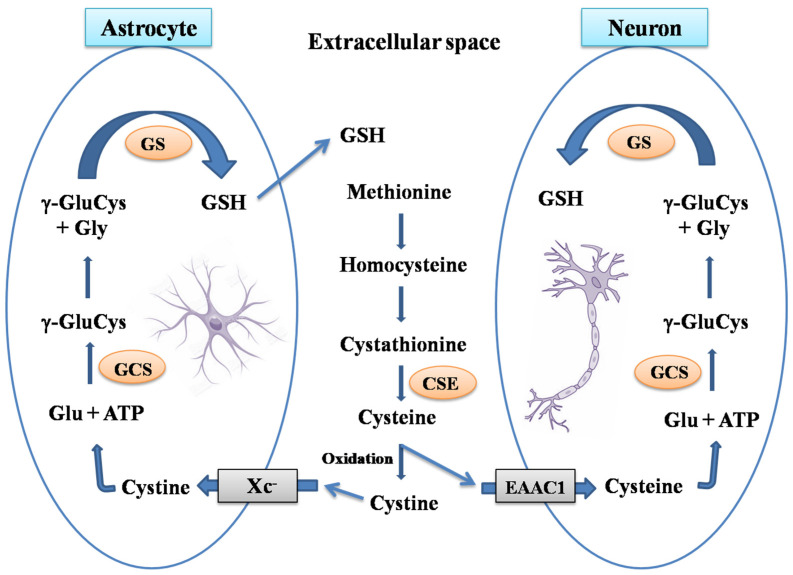
Figure 2.
GSH synthesis in astrocytes and neurons. The Transsulfuration pathway synthesizes homocysteine from the dietary amino acid methionine to produce cystathionine. Further, cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) converts cystathionine into cysteine in extracellular to neurons and astrocytes. Neurons utilize extracellular cysteine for GSH synthesis, unlike astrocytes which uses the oxidized form cystine. Neurons uses excitatory amino acid transporter (EAATs) to take up cysteine, while a cystine/glutamate transporter (Xc-) mediates the transport of cystine in astrocytes. γ-Glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS), rate limiting enzyme in GSH synthesis catalyzes the formation of γ-glutamylcysteine dipeptide utilizing ATP. γ-GluCys is then combined with glycine to form GSH by glutathione synthetase (GS) in both neurons and astrocytes. GSH formed in astrocytes is released into extracellular space where it is cleaved into individual aminoacids by a set of enzymes.