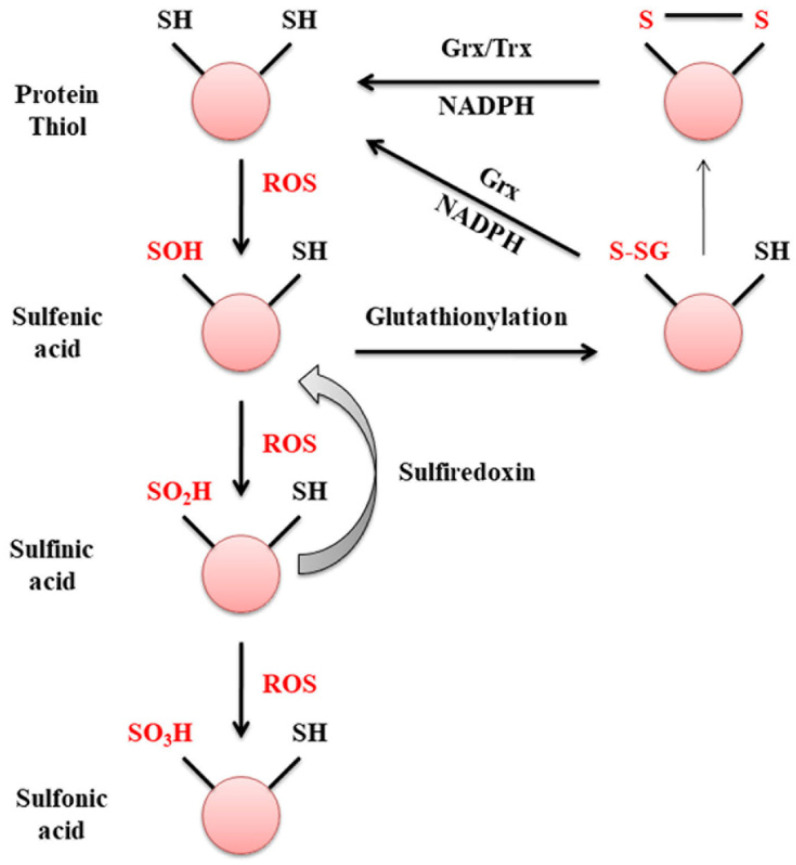
Figure 3.
Oxidation of protein thiols to sulfonic acids. During oxidative stress, ROS such as hydrogen peroxide can catalyze the two-electron oxidation of sulfur present in amino acid cysteine. Protein thiols are oxidized to sulfenic acid, which can react with GSH to form protein disulfide preventing further oxidation. Pr-SSG formed is reduced back to active thiols by glutaredoxin or thioredoxin using reducing equivalent NADPH. Sulfinic acid formed by subsequent oxidation of sulfenic acid is still reversible by the reductase enzyme, sulferedoxin. Further oxidation of sulfinic acid results in an irreversible formof sulfonic acid, which targets the protein for degradation.