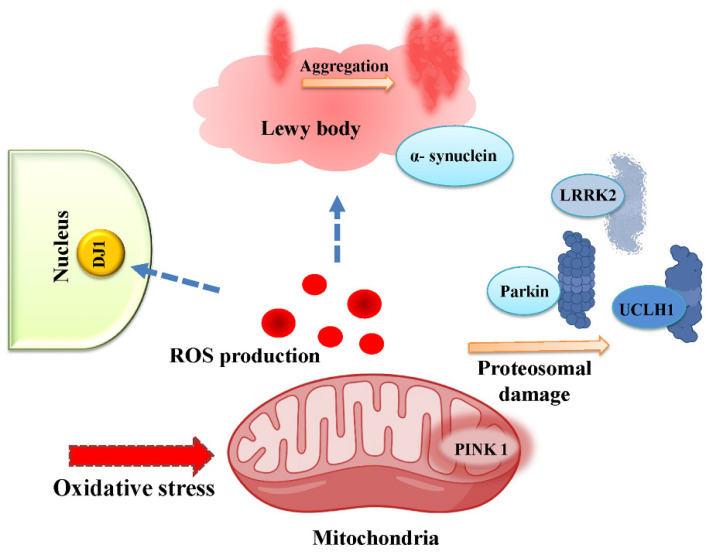
Figure 5.
Familial PD genes link mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production to PD pathology. Pink1 is a mitochondrial serine/threonine protein kinase that promotes mitophagy in depolarized mitochondria. PINK1 mutation affects mitochondrial respiration along with DA neuron loss and Lewy pathology. α-synuclein deposition in neurons or mitochondria and loss of parkin function increases oxidative stress, alters mitochondrial membrane potential, complex Ⅰ function and mitochondrial morphology. DJ-1 is involved in response to oxidative stress and may be neuroprotective. Mutations in DJ-1 increase ROS production, accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria and loss of membrane potential [69]. Mutations in the LRRK2 gene, a common cause of familial and sporadic PD affect mitochondrial dynamics, trafficking and degradation via autophagy [72].