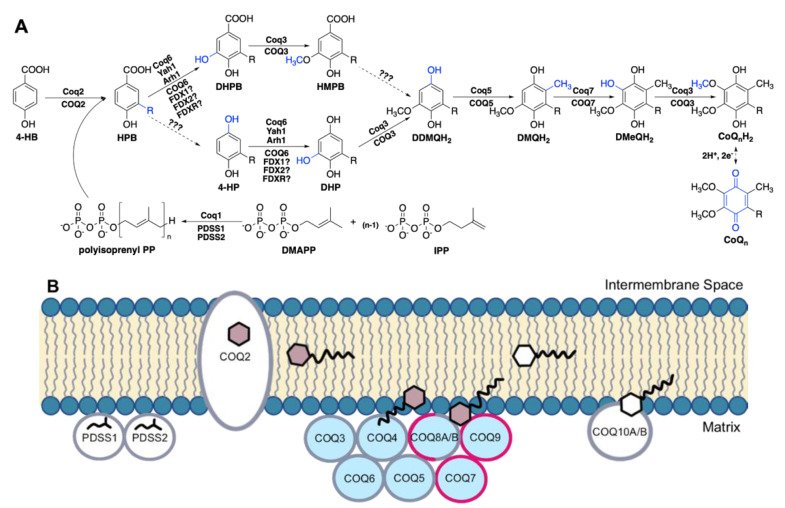
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of coenzyme Q. (A) The CoQ biosynthetic pathway is largely homologous between S. cerevisiae (polypeptide names above arrows) and humans (polypeptide names below arrows). In humans, at least seven nuclear-encoded catalytic proteins are directly responsible for the biosynthesis of CoQ from 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4-HB), a tyrosine derivative. The enzyme(s) responsible for the decarboxylation and hydroxylation step(s) (dashed arrows) at ring position 1 has not been found. Hence, there is uncertainty about the order of steps. The decarboxylation step may precede the Coq6/COQ6 hydroxylation step based on the accumulation of 4-hydroxy-3-polyprenylphenol (4-HP) in yeast and human cells harboring mutations in Coq6/COQ6 data from [14,33,34]. In addition to the yeast Coq and human COQ polypeptides, other polypeptides involved in CoQ biosynthesis include PDSS1 and PDSS2 (decaprenyl diphosphate synthase subunits 1 and 2), Yah1 (yeast ferredoxin), Arh1 (yeast ferredoxin reductase), FDX1 and FDX2 (human ferredoxins 1 and 2), and FDXR, human ferredoxin reductase. Intermediates in the pathway include: DMAPP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; HPB, 3-polyprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid; DHPB, 4,5-dihydroxy-3-polyprenylbenzoic acid; HMPB, 4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3-polyprenylbenzoic acid; DHP, 4,5-dihydroxy-3-polyprenylphenol; DDMQH2, 2-methoxy-6-polyprenyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone; DMQH2, 2-methoxy-5-methyl-6-polyprenyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone; DMeQH2, 3-methyl-6-methoxy-2-polyprenyl-1,4,5-benzenetriol. Note that the intermediates found in S. cerevisiae contain a hexaprenyl tail, while humans make decaprenylated CoQ10 intermediates. (B) The CoQ synthome (Complex Q in humans) is a high-molecular mass protein and lipid complex data from [1], consisting of polypeptides COQ3-COQ9. The PDSS proteins (homologous to S. cerevisiae Coq1), COQ2, and the lipid-binding proteins COQ10A and COQ10B do not associate with the complex. Colored hexagons indicate CoQ intermediates; white hexagons indicate the final CoQ product. Polypeptides for which the human protein structures have been solved are highlighted in pink. The COQ8A/COQ8B polypeptides are thought to have a dynamic association with complex Q. Polypeptides are not drawn to scale and their stoichiometry has not been determined.