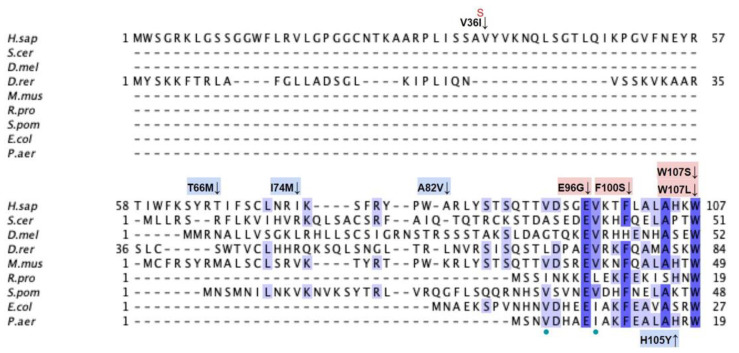
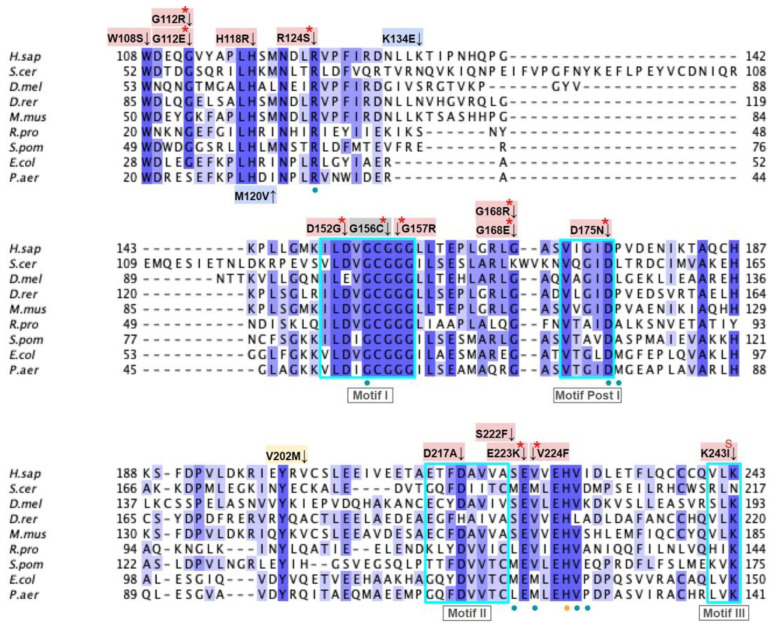
Figure 3.
Labeled and annotated multiple sequence alignment of COQ3. Amino acid sequences of COQ3 were analyzed as described in Materials and Methods and include Homo sapiens (NCBI accession number NP_059117.3) and homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (NP_014545), Drosophila melanogaster (NP_610092.2), Danio rerio (NP_001002620.1), Mus musculus (NP_766275.1), Rickettsia prowazekii (WP_004596275.1), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (NP_588239.2), Escherichia coli (NP_416735.1), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (WP_003122245.1). See KEY for descriptions of the figure annotations. Putative AdoMet binding residues are denoted by a blue dot, and residues thought to interact with the cell membrane in E. coli UbiG are denoted by a purple dot, data from [45,46]. A pair of co-evolving, highly conserved, and structurally nearby histidines may be involved in metal ion coordination (orange dot), data from [63]. Methyltransferase motifs I, post-I, II, and III are boxed in cyan data from [56,64]. The putative membrane-interacting hydrophobic region is boxed in red, data from [45]. For all multiple sequence alignments, conservation is indicated via shaded residues, which represent a percent identity great than 80%, 60%, and 40%, from darkest to lightest. Residues with less than 40% identity are unshaded.