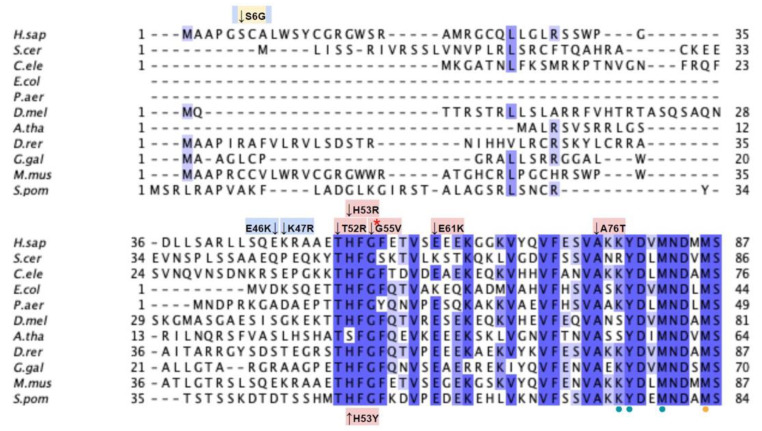
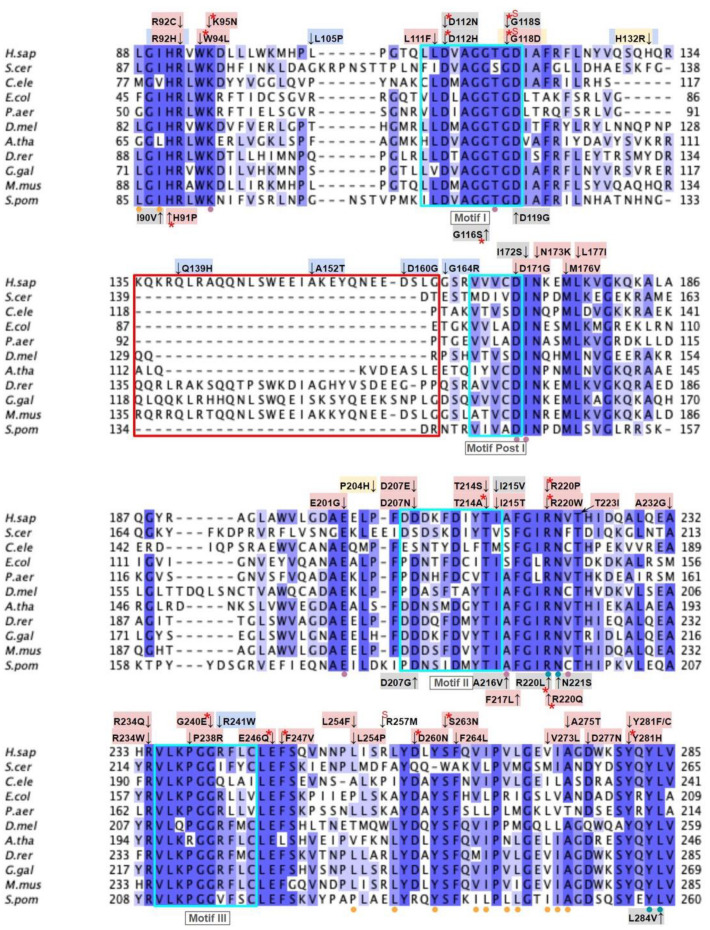
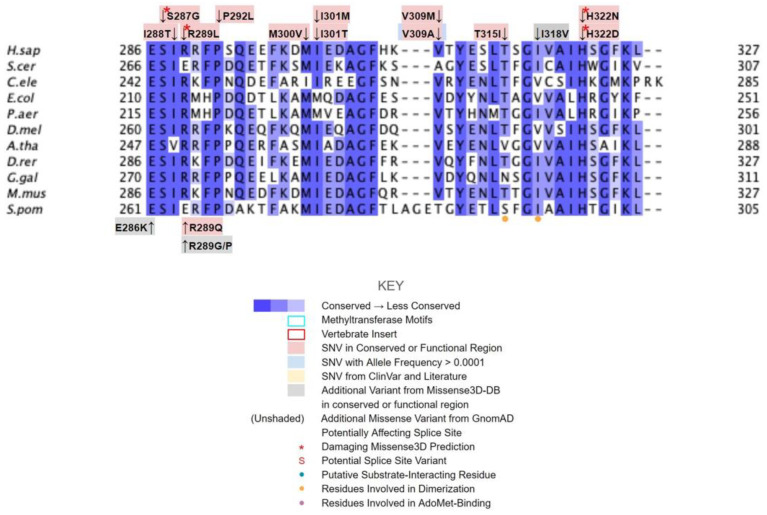
Figure 12.
Labeled and annotated multiple sequence alignment of COQ5. Amino acid sequences of COQ5 were analyzed as described in Materials and Methods and include Homo sapiens (NCBI accession number NP_115690.3) and homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (NP_013597.1), Caenorhabditis elegans (NP_498704.1), Escherichia coli UbiE (YP_026260.1), Pseudomonas aeruginosa UbiE (NP_253750.1), Drosophila melanogaster (NP_572865.1), Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_200540.1), Danio rerio (NP_001004541.1), Gallus gallus (NP_001006194.1), Mus musculus (NP_080780.1), and Schizosaccharomyces pombe (NP_587834.1). See KEY for descriptions of the figure annotations. Functional residues (dotted) were determined from the yeast Coq5 crystal structure (data from [48]). Methyltransferase motifs I, post-I, II, and III are boxed in cyan (data from [18]). An insert exclusively found in vertebrate species is boxed in red. Note that W243 in S. cerevisiae (aligned to S263 in the human sequence) is the residue involved in dimerization based on the crystal structure. However, since all other species in the multiple sequence alignment have a Tyr insertion at that position, Y262 was chosen as the functional residue instead due to its similar aromatic nature.