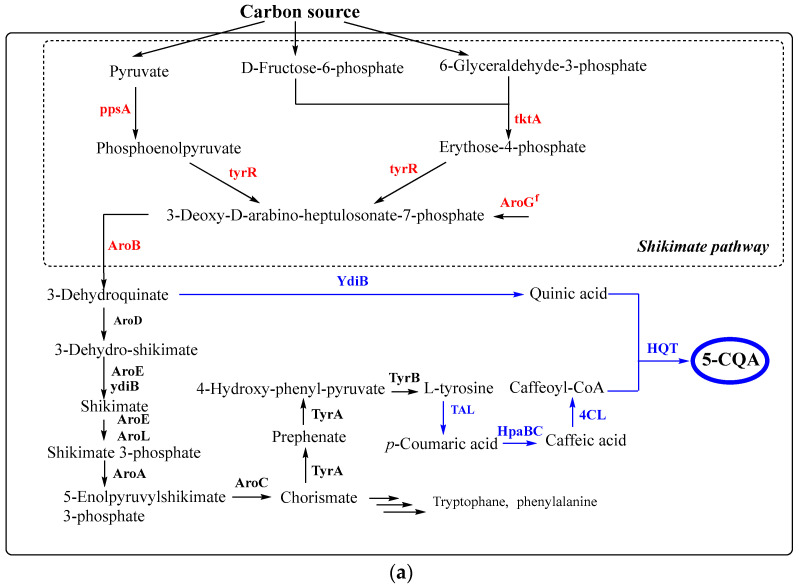
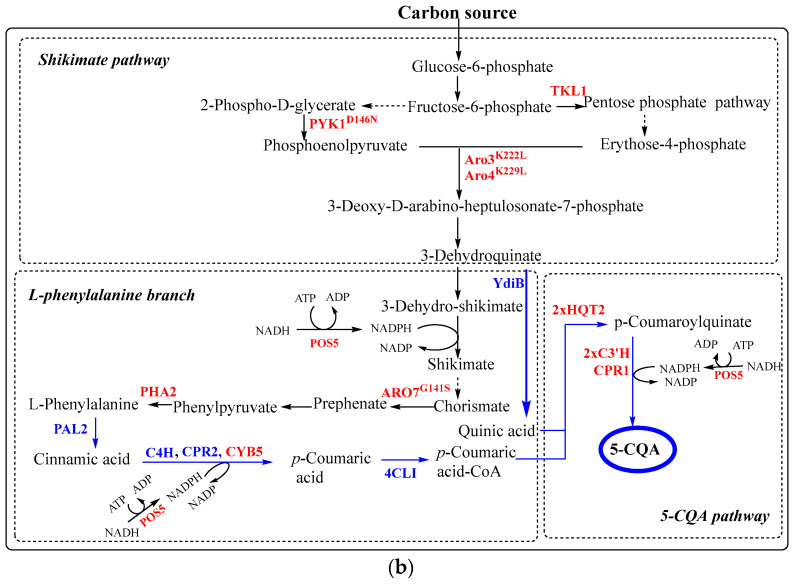
Figure 6.
The synthesis of chlorogenic acid in E. coli (a) and S. cerevisiae (b) from carbon source according to [146; 151]. Black and blue arrows correspond to native and non-native pathways, respectively. Dashed arrows represent the complex processes. The blue and red names of genes correspond to inserted and overexpressed genes, respectively. Abbreviations: AroH - phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase; TyrR—transcriptional regulatory protein; AroF - phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase; AroG—phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase; AroD—5-dehydroquinate dehydratase; AroB—dehydroquinate synthase; PAL2—phenylalanine ammonia lyase from Arabidopsis thaliana; C3′H—cytochrome P450 98A3 from A. thaliana; CPR1 and AtCPR2—P450 reductases from A. thaliana; YdiB—quinate/shikimate dehydrogenase from E. coli; AtC4H, cinnamate-4-hydroxylase from A. thaliana; 4CL—4-coumarateCoA:ligase from Oryza sativa; 4CL1, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase 1 from A. thaliana; HQT—hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA quinate transferase from Nicotiana tabacum; HQT2—hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA quinate transferase 2 from Cynara scolymus; ARO3K222L—l-phenylalanine feedback-insensitive DAHP synthase; ARO4K229L—l-tyrosine feedback-insensitive DAHP synthase; ARO7G141S—l-tyrosine feedback-insensitive chorismate mutase; PYK1D146N—pyruvate kinase 1 mutant with reduced catalytic activity.