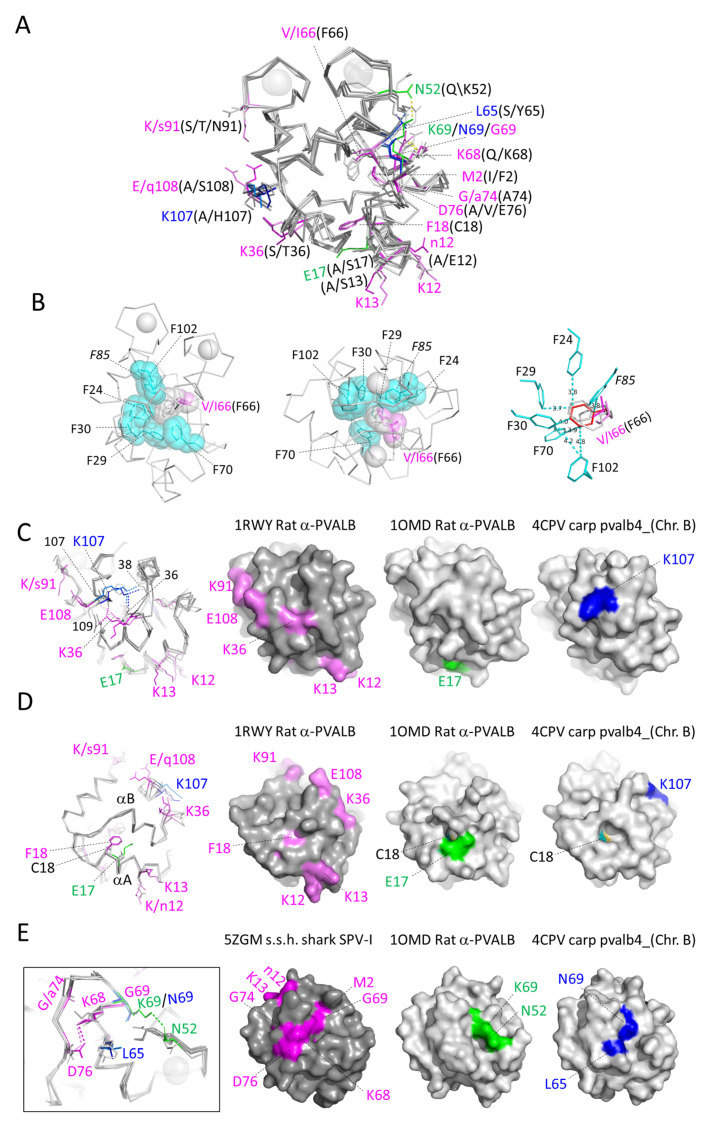
Figure 9.
Structural locations of residues that are rather characteristic for the α-parvalbumins, oncomodulins, or other parvalbumins. Sidechains of residues at positions with category-specific features are shown in sticks format, in color when they are category-specific and otherwise in gray. Superimposition of X-ray crystallography structures of α-parvalbumin (lineage-specific sidechains in violet, rat α-parvalbumin [1RWY]; magenta, spotless smooth-hound shark SPV-I [5ZGM]), oncomodulin (sidechains in green, rat oncomodulin [1OMD]), and other parvalbumins (sidechains in marine blue, chicken ATH [3FS7]; blue, common carp pvalb4_[Chr.A3] [4CPV]). (A) In this figure, all the residues at the relevant positions are named. Most of the category-specific residues are located outside of the molecules, but the (V/I/F)66 and (C/F)18 residues are among the exceptions and reside (mostly) within the inner part of the molecules. (B) In α-parvalbumins one phenylalanine, at position 66, is lacking from an inner core set of phenylalanines compared to the other parvalbumin categories. Apart from the residues at position 66, this figure only shows common carp pvalb4_(Chr.A3) residues. F85 is only rather well conserved throughout parvalbumins (it is not highlighted with gray or black in Figure 3), which is why it is indicated in Italic font. Apart from in sticks format, in the two figures at the left (which show the same from different angles) the relevant sidechains are also highlighted in transparent spheres format. In the figure at the right, with carp pvalb4_(Chr.A3) F66 in red, the distances in Å between several atoms of the carp pvalb4_(Chr.A3) phenylalanines are indicated. (C) The sidechain of α-parvalbumin-specific K36, located in the BC-loop, makes polar contacts (dashed lines) with the main chains of residues 107 and 109 at the C-terminus of the molecule. The sidechain of non-α/non-oncomodulin category-specific K107, in α-helix F, makes polar contacts with the main chains of residues 38 and 36 in the BC-loop. On the right, with a similar molecule orientation and coloring as in the superimposition figure on the left, the surface structures of one molecule per category are shown. (D) At position 18, α-parvalbumins have a phenylalanine whereas most other parvalbumins have a cysteine. In either case, the residue points from near the C-terminal end of α-helix A to the molecule interior under α-helix B and is mostly covered. In the surface figures at the right, the C18 residue is colored with cyan for carbon and yellow for sulfur. (E) In α-parvalbumins, polar contacts are formed between the sidechains of lineage-specific K68 in α-helix D and D76 in the DE-loop. In rat oncomodulin, polar contacts are formed between the sidechains of lineage-specific residues N52 in the CD-loop and K69 in α-helix D.