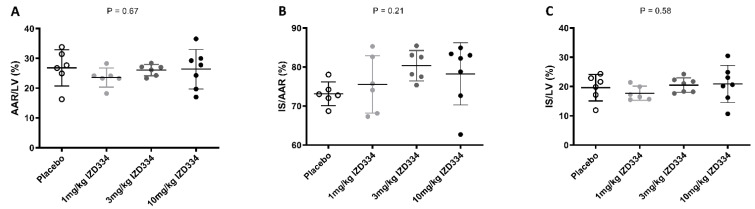
Figure 6.
Myocardial infarct size. Normal distribution of data was confirmed as described in our methods (using Shapiro–Wilk test). Hence, a one way-ANOVA was performed. (A) The area at risk as a ratio of the left ventricle (AAR/LV) was similar in all treatment groups (placebo 26.8 ± 6.1%, 1 mg/kg IZD334 23.5 ± 3.2%, 3 mg/kg IZD334 26.0 ± 1.9%, 10 mg/kg IZD334 26.4 ± 6.6%, ANOVA, p = 0.67) groups (p = 0.67). (B) The infarct size (IS) was not different between treatment groups when expressed relative to measurements of the ischemic AAR (placebo 73.1 ± 3.0%, 1 mg/kg IZD334 75.5% ± 7.3%, 3 mg/kg IZD334 80.3 ± 3.9%, 10 mg/kg IZD334 78.2% ± 8.0%, ANOVA p = 0.21). (C) IS as percentage of the LV did not differ (placebo 19.6 ± 4.5%, 1 mg/kg IZD334 17.7 ± 6.3%, 3 mg/kg IZD334 20.5 ± 2.2%, 10 mg/kg IZD334 19.3 ± 2.9%, ANOVA p = 0.58). N.B. In one pig of the 3 mg/kg group, it was not possible to measure the AAR due to a failure to infuse Evans Blue in the coronary arteries. Therefore, only in 6 pigs could the AAR and the IS/AAR be shown.