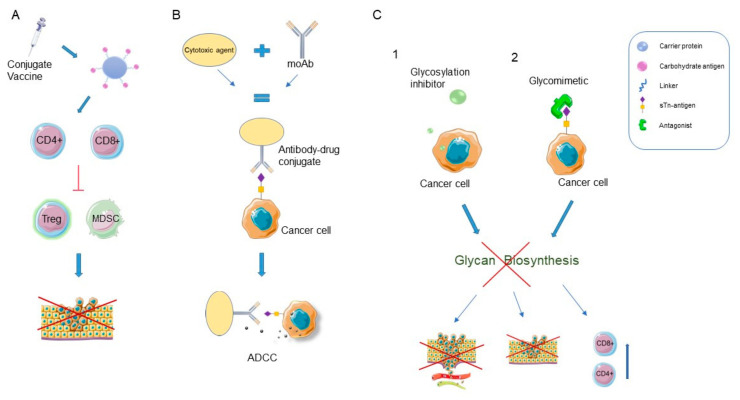
Figure 1.
Glycan-based therapies. (A) Carbohydrate vaccine induces a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and anti-tumor immunity by reducing the function of immunosuppressive cells (Treg and MDSC) and inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells. (B) Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are targeted agents that combine less specific chemotherapeutic agents with glycan-specific antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies (moAbs) promote antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). (C1) Glycosylation inhibitors are small molecules that can interfere with metabolism of precursors or intracellular activities; (C2) Glycomimetics selectively block glycan receptors on the surface of cancer cells. Glycosylation inhibitors and glycomimetics interfere with glycan biosynthesis, preventing cancer cell adhesion to endothelial cells, metastasis, and enhancement of cytotoxic T cell immunity. CD4+—Helper T cell; CD8+—cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Treg—regulatory T cell; MDSC—myeloid-derived suppressor cell. Figure created with Servier Medical Art, https://smart.servier.com/ accessed on 20 July 2022.