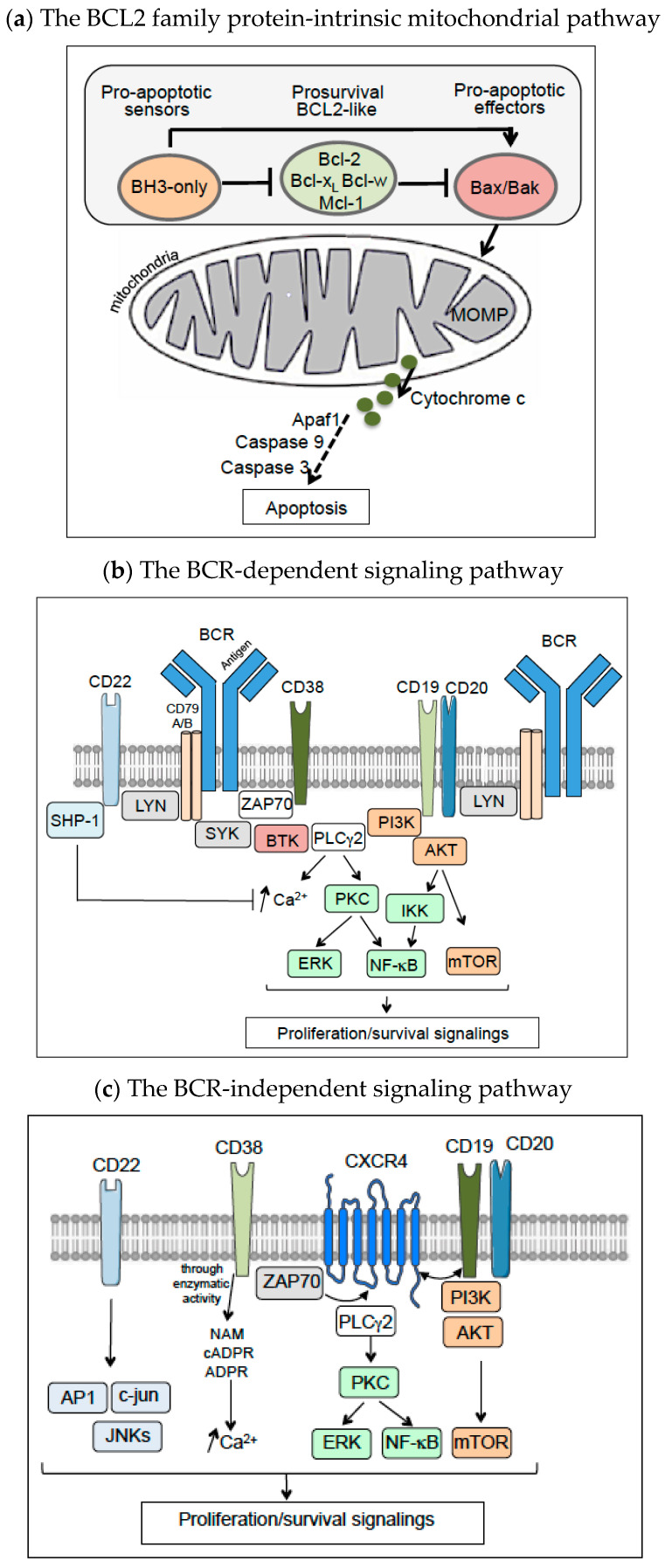
Figure 1.
Models for the signaling pathways regulated by BCL2 family proteins, BCR components, and TAAs (CD19, CD20, CD22, CD38) in B cell malignancies. (a) Prosurvival BCL2-like proteins (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Bcl-w, and Mcl-1) interact with the proapoptotic members called BH3-only proteins (Bim, Bid, Puma, Bad, and Noxa), or bind to the apoptotic effectors Bax and Bak and sequester them in an inactive form. The pro-apoptotic proteins induce apoptosis by activating Bax and Bak either directly or indirectly through inhibition of the anti-apoptotic proteins. Once activated, Bax and Bak form oligomers; this leads to pore formation, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), and then the release of cytochrome c and other pro-death proteins from mitochondria, resulting in caspase activation and cell apoptosis. (b) Upon BCR ligation and activation, Lyn phosphorylates CD79A/B, which activates SYK. In turn, activated SYK phosphorylates and recruits the B-cell linker protein (BLNK), which binds to BTK and PLCγ2 and catalyzes the cleavage of membrane phosphatidyl inositol bisphosphate into inositol triphosphate and diacyl glycerol. This releases Ca2+ from intracellular stores and activates PKCβ and downstream proteins. The positive BCR coreceptors CD19 and CD20 are phosphorylated by LYN during BCR signaling, leading to the recruitment of PI3K to the BCR. Together, these signaling pathways activate the ERK, NF-κB, AKT/mTOR pathways. The negative B cell coreceptor CD22 is phosphorylated by LYN and inhibits the BCR signal by recruiting SHP-1, which dephosphorylates and inactivates BLNK and CD19 and thus leads to a decrease in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration. SHP-1 also decreases the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration by activating the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA4) and thus promoting Ca2+ efflux. CD38 activation leads to the phosphorylation of ZAP70 and further sustains the signal mediated by the BCR. (c) Independently of the BCR signaling pathway, CD19, CD20, CD22, and CD38 have a role in activating proliferation/survival pathways in malignant B cells. CD38 (via ZAP70 activation), CD19 and CD20 are linked to the proliferation/survival signaling pathways controlled by CXCR4. Through CD38′s enzymatic activity, the reaction products (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, cyclic ADP-ribose, and ADP-ribose) are used inside the cells to open different Ca2+ stores, which leads to an increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration independently of the conventional IP3 pathway. CD22 ligation activates AP-1, c-jun, and the c-jun NH2-terminal kinases (JNKs).