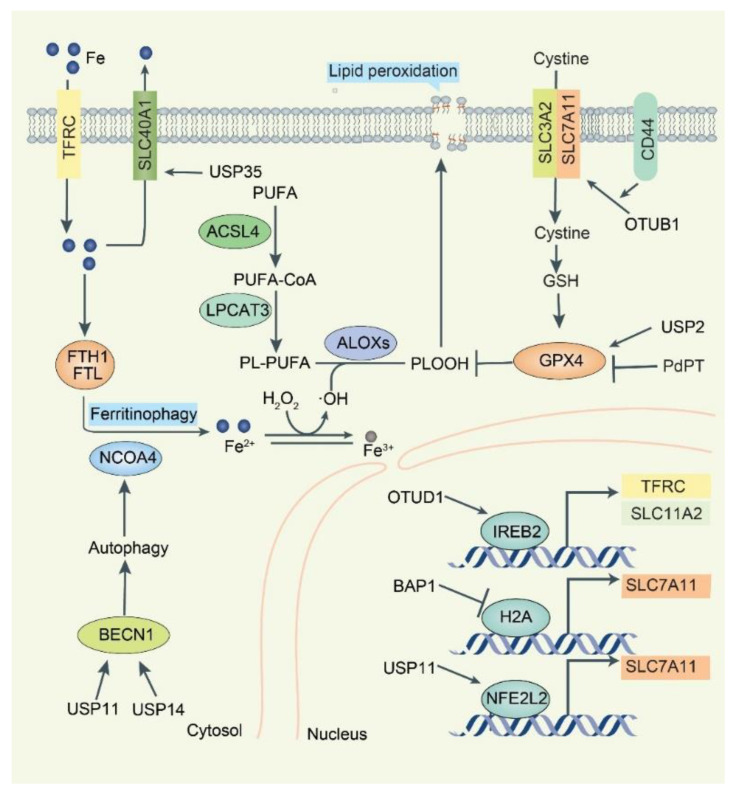
Figure 4.
Overview of DUBs-mediated regulation of ferroptosis. Induction of iron-mediated ferroptosis depends on disruption of the balance of oxidants and antioxidants. SLC40A1 is the only cellular iron exporter. USP35 binds to SLC40A1 to stabilize its expression and inhibit ferroptosis. TFRC uptakes extracellular iron and stores iron through FTH1/FTL. Cell-destabilizing iron release from ferritin is dependent on NCOA4-dependent ferrotinophagy. Labile iron promotes the production of PL-OOH, which leads to membrane lipid oxidation and cell death. BECN1 promotes autophagy and ferrotinophagy. Two DUBs, USP11 and USP14, are responsible for BECN1 deubiquitination. SLC7A11 and SLC3A2 form the amino acid transport system xc–, which uptakes cystine into the cytosol, where it is rapidly converted to cysteine and used for glutathione synthesis. The stem cell marker CD44 promotes OTUB1-SLC7A11 association and stabilizes SLC7A11. Selenium enzyme GPX4 reduces PLOOH and inhibits ferroptosis via glutathione. DUB USP2 stabilizes GPX4, and the pan-DUBs inhibitor PdPT promotes GPX4 degradation. The transcription factor IREB2 is responsible for TFRC and SLC11A2 gene transcription. DUB OTUD1 binds and stabilizes IREB2, while BAP1 promotes SLC7A11 transcription through histone H2A deubiquitination. NFE2L2 is responsible for SLC7A11 transcription and USP11 stabilizes NFE2L2 protein.