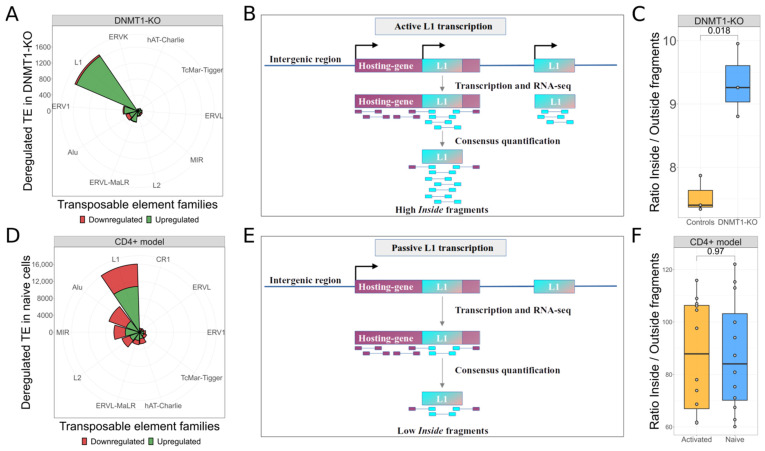
Figure 1.
The KO of DNMT1 gene leads to autonomous L1 transcription. (A). Top-10 deregulated TE families in DNMT1 model. L1 is the most upregulated TE family with 1660 elements. (B). Rationale of our method for detecting autonomous transcription of L1 elements. Autonomous transcription of L1s will produce a higher amount of Inside fragments with both reads mapped inside the L1 consensus resulting in a higher Inside/Outside ratio. (C). Analysis to detect autonomous transcription of L1 elements. Upon the KO of DNMT, the upregulation of L1s derives by autonomous transcription of elements. (D). Top-10 deregulated TE families in naive T CD4+ cells. L1 is the most upregulated TE family with 10,794 elements. (E). Rationale of our method for detecting non-autonomous transcription of L1 elements. Transcription of L1s embedded in other transcriptional units will produce a low amount of Inside fragments. (F). Analysis to detect autonomous transcription of L1 elements. In naive T CD4+ cells, the upregulation of L1s derives by a non-independent transcription of elements. Given that the two distributions are similar the overexpression of L1s is due to their transcription as part of other transcriptional units.