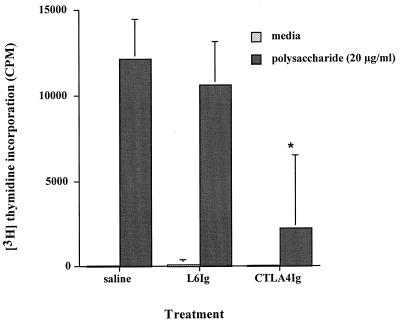
FIG. 1.
Effect of CTLA4Ig on polysaccharide-mediated CD4+ T-cell proliferation in vitro. Addition of CTLA4Ig (50 μg/ml) to human T cells and irradiated APCs cultured with the S. pneumoniae type 1 CP (20 μg/ml) for 6 days resulted in a significant decrease in activity (P < 0.006 compared with the saline control [∗]). Addition of L6Ig at a similar concentration did not have this effect. Error bars indicate standard deviations.