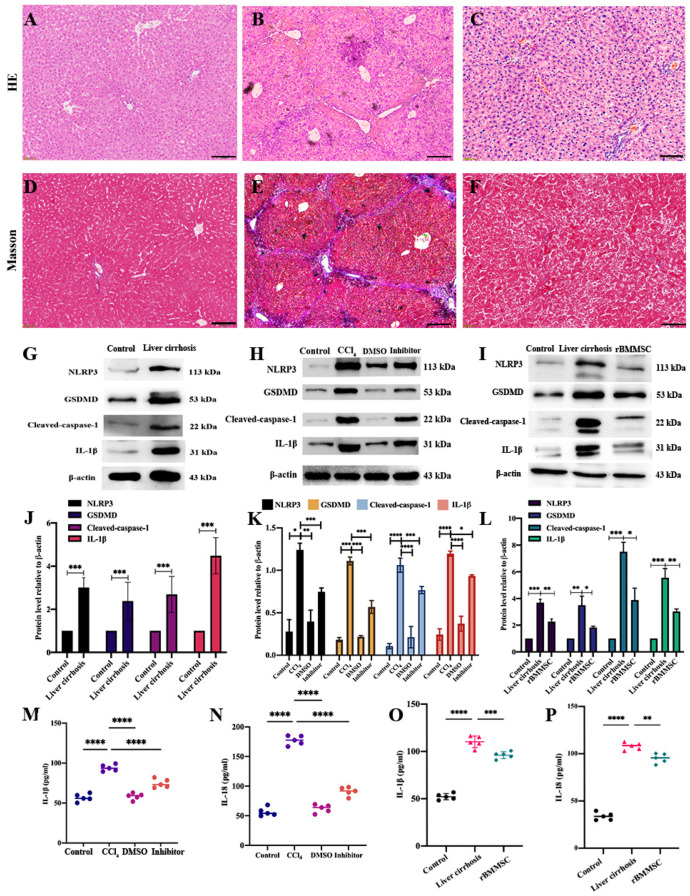
Figure 1.
The alleviation of pyroptosis by rBMMSCs in the context of liver cirrhosis. Pathological HE- and Masson-stained sections of control and cirrhotic liver tissues are shown (A–F). Pathological sections showed significant alleviation in the rBMMSC transplantation group (B,C). Scale bar = 100 μm applied to (A–F). Pyroptosis-related proteins (NLRP3, GSDMD, cleaved caspase-1 and IL-1β) were markedly highly expressed in the liver cirrhosis model ((G,J), *** p < 0.001 vs. the control). The disulfram inhibited the expression of pyroptosis-related proteins, as shown in (H). The expression levels of pyroptosis-related proteins in the inhibitor group were significantly decreased compared to those in the CCl4 group ((K), * p < 0.05). The IL-1β and IL-18 expression in the inhibitor group were significantly down-regulated compared to those in the CCl4 group ((M,N), **** p < 0.0001). Pyroptosis-related proteins in the BMMSC group were significantly down-regulated compared to those in the liver cirrhosis group ((I,L), * p < 0.05). IL-1β and IL-18 expression in the BMMSC group were dramatically decreased ((O,P), ** p < 0.01 vs. the liver cirrhosis group). The data are displayed as the means ± SD; n = 5 for each group.