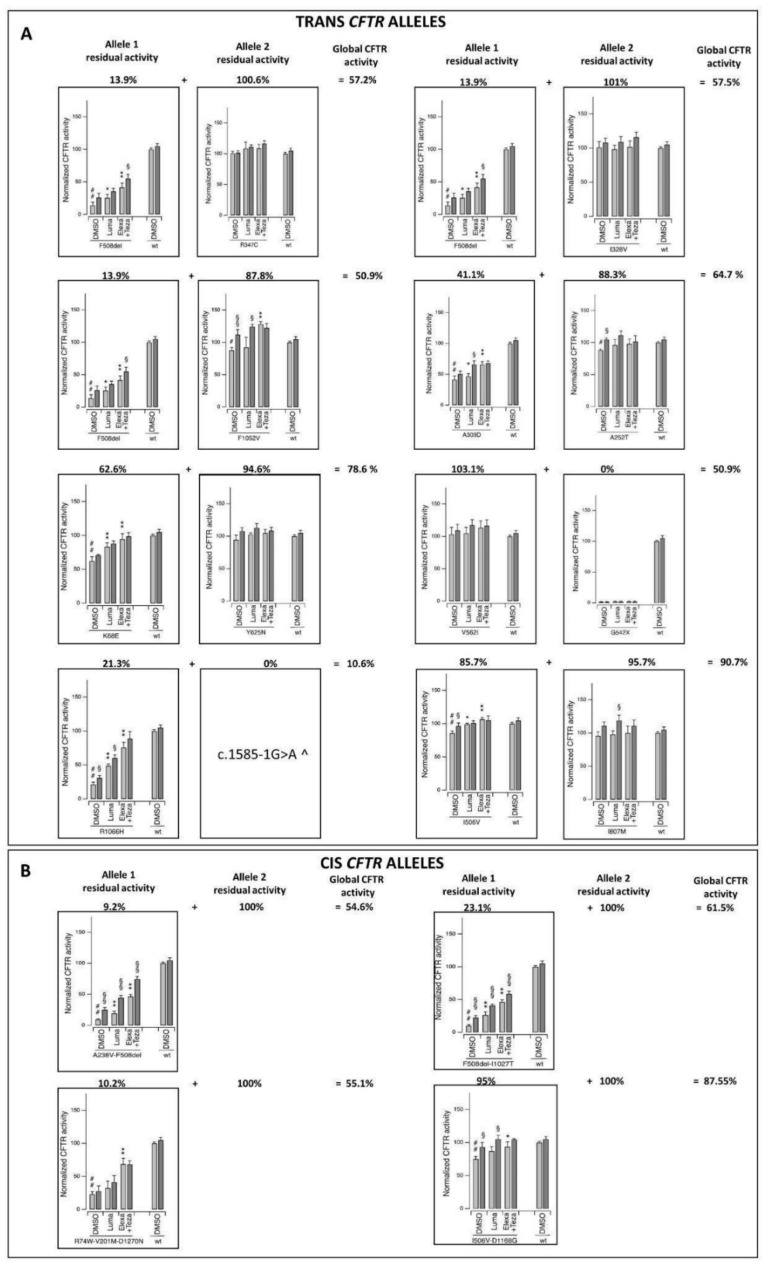
Figure 3.
Functional analysis of CFTR ultra-rare variants on heterologous expression systems identified loss-of-function alleles with reduced activity. (A) Functional analysis of trans CFTR alleles. (B) Functional analysis of cis CFTR alleles. The bar graphs show the activity of the different CFTR variants under investigation and, for comparison, WT-CFTR transiently expressed in CFBE41o- cells stably expressing HS-YFP. CFTR activity was determined as a function of the YFP quenching rate following the iodide influx in the cells stimulated with FSK alone (20 µM; light gray) or with FSK plus ivacaftor (1 µM; dark gray). The data are means ± SD (n = 3). The symbols indicate the statistical significance: # p < 0.05 vs. WT-CFTR protein; ## p < 0.01 vs. WT-CFTR protein; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. DMSO-treated, FSK-stimulated variant protein; §, p < 0.05, §§, p < 0.01 vs. FSK-stimulated variant protein (upon the same chronic treatment). ^ this type of variant is expected to result in little or no CFTR protein (see CFTR2 database at https://cftr2.org, accessed on 3 November 2022).