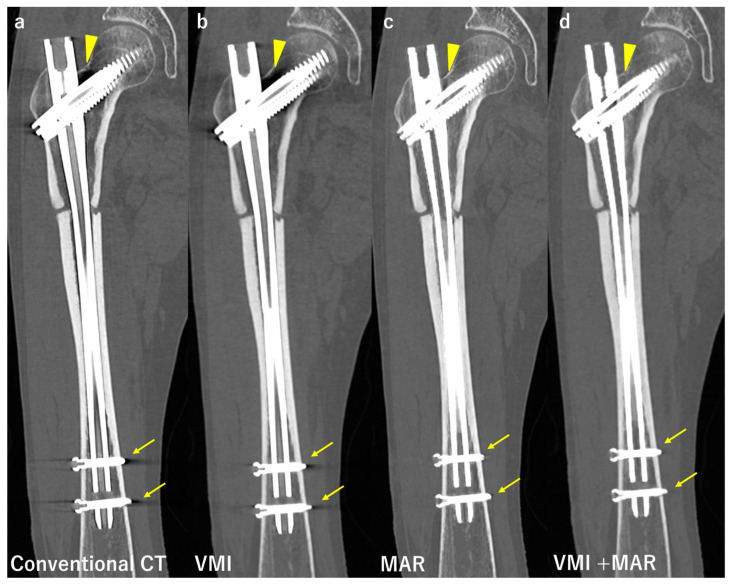
Figure 5.
Comparison of conventional computed tomography (CT) and images reconstructed with virtual monoenergetic images (VMI), the metal artifact reduction algorithm (MAR), and combination of VMI and MAR. Coronal images of a patient after intramedullary nail fixation of the femur. Image (a) was taken by conventional CT at 120 kV, and shows strong beam hardening, scattering, photon starvation, and edge effects at the junction of the nail and lag screw (arrowheads), and at the tip of distal locking screws (arrows). Image (b) was taken by VMI at 135 kV, and the artifacts are slightly reduced, especially at the tip of distal locking screws. Image (c) was taken with MAR, and the artifact reduction is stronger than VMI, only very small dark streaks both at the junction of the nail and lag screw and at the tip of distal locking screws. Image (d) was taken in combination with VMI at 135 kV and MAR, and there are almost no artifacts present, leading to a better visualization of the outlines of the prosthesis.