TABLE 2.
Summary of classification methods used for the food-recognition task in image-based food-recognition systems
| Classification method | Depiction | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
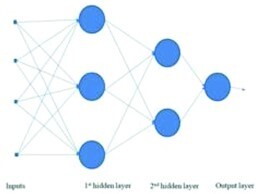
| Artificial neural network (ANN) |
|
|
|
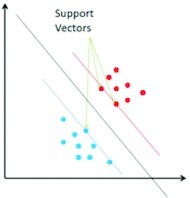
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) |
|
|
|
| Naive Bayes (NB) |
|
|
|
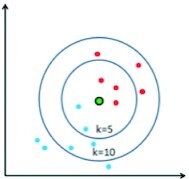
| K-nearest neighbor (KNN) |
|
|
|
| Random forest (RF) |
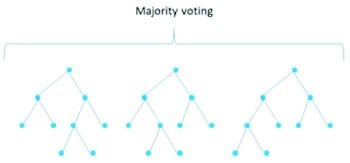
|
|
— |
| Convolutional neural network (CNN) |
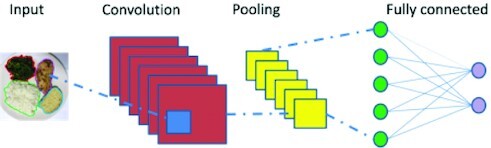
|
|
|
