Figure 5. Immunofluorescence localization of NKCC1 and BKα channel specific proteins in normal and dietary Na+-depleted rat distal colon.
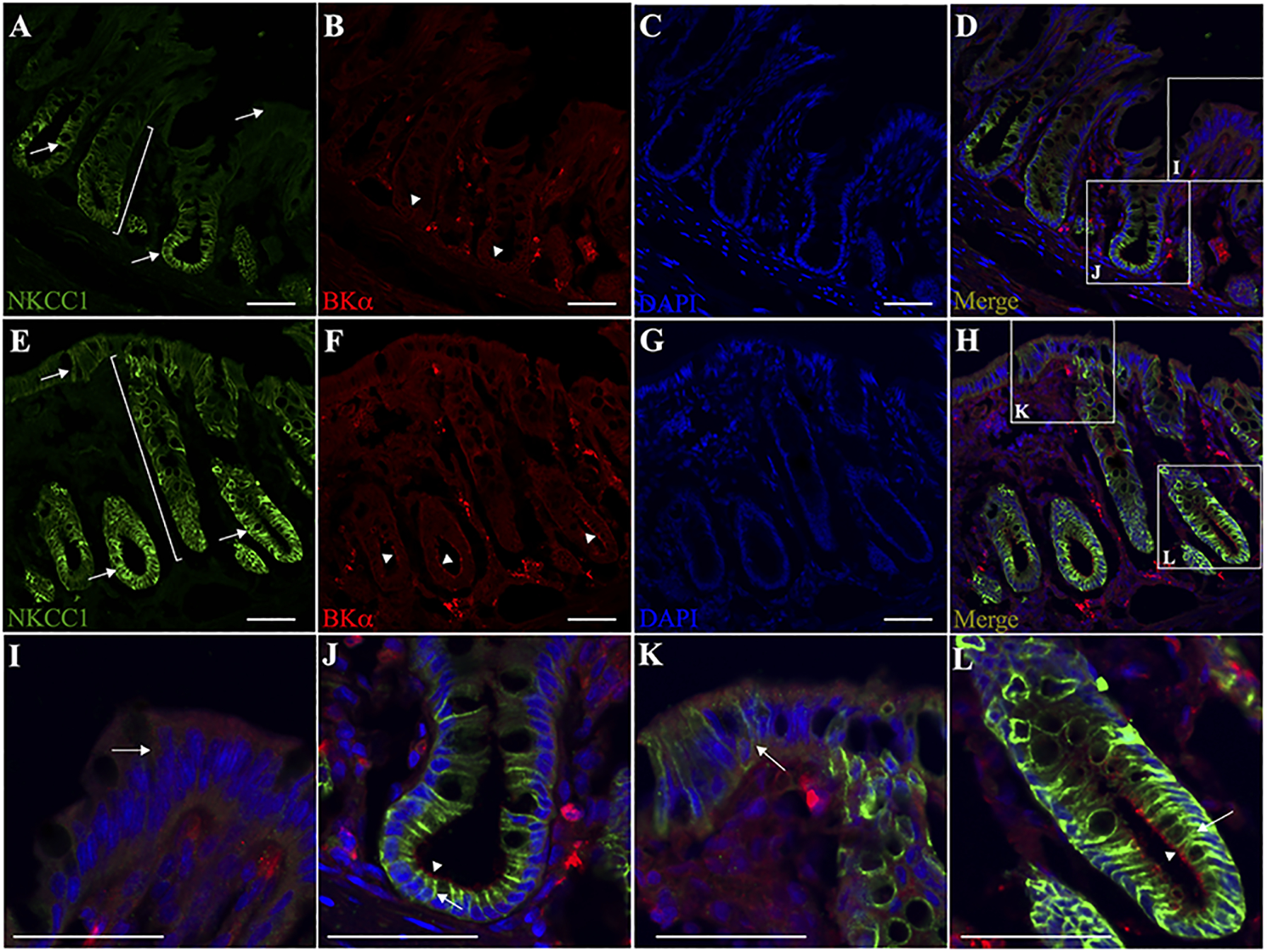
Normal (A-D) and dietary Na+-depleted (E-H) rat distal colon sections were labelled with both anti-NKCC1 (green) and anti-BKα (red) antibodies, while nuclei were labelled with DAPI (blue). Merged images are shown in panels D and H. All images were captured at 20x magnification, scale bar = 50 μm. Magnified surface cell regions are shown for normal (I) and dietary Na+-depleted (K) rat distal colon images, as indicated by the white boxes in panels D and H. Magnified crypt regions are also shown for normal (J) and dietary Na+-depleted (L) rat distal colon. Arrows indicate basolateral membrane labelling of NKCC1 in the lower crypt region of normal (A,J), and the whole crypt as well as surface cells in Na+-depleted rat distal colon sections (E,K,L). Brackets in panels A and E illustrate that NKCC1 labelling appears mostly restricted to the lower crypt in normal, while extending upward to the surface region in Na+-depleted rat distal colon. Arrowheads indicate the apparent mucosal membrane-localized BK channels in the crypts of both normal (B,J) and Na+-depleted (F,L) rat distal colon sections, while BK labelling in the surface regions was diffuse in both normal and Na+-depleted colon sections.
