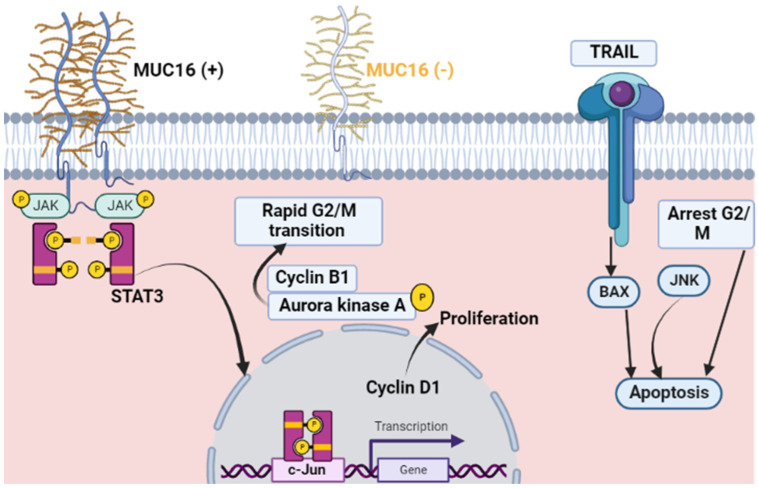
Figure 1.
MUC16 expression in cancer: The MUC16 expression (+) stimulates tumor cell division via its binding to the non-receptor tyrosine kinase JAK2, which stimulates transcription factor STAT3 phosphorylation, which activates the expression of c-Jun for Cyclin D1. MUC16 influences the G2/M transition process via Cyclin B1 and phosphorylation of Aurora kinase A. Reduced expression of MUC16 (−) leads to malignant cells accumulation during the cell cycle’s G2/M phase with subsequent apoptosis of breast cancer cells via JNK signaling.