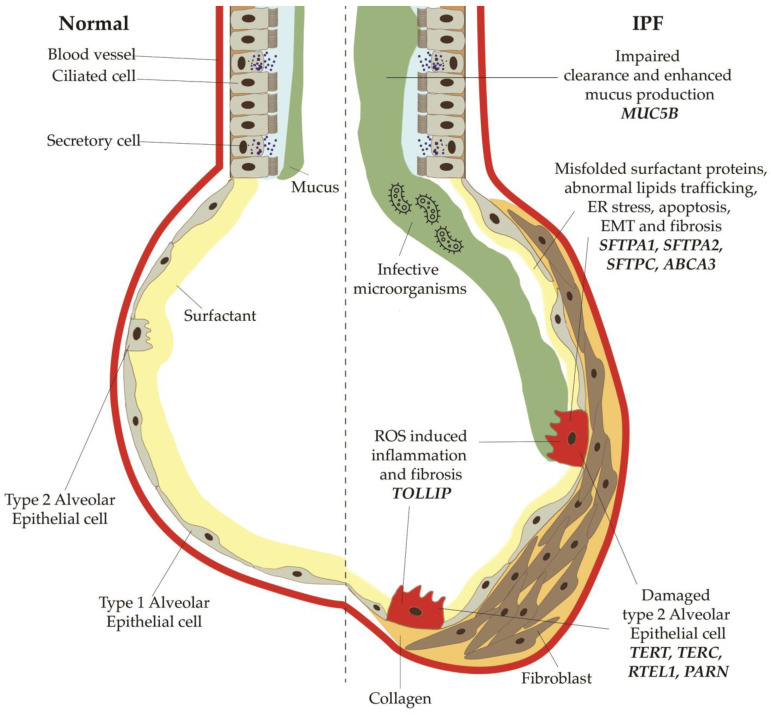
Figure 2.
Main profibrotic mechanisms secondary to mutations or polymorphisms in the genes for telomerases, surfactant proteins, mucin 5B. Mutations in TERT, TERC, PARN and RTEL1 decrease the activity of telomerase, thus resulting in augmented shortening of telomeres. SFTPC, SFTPA1, SFTPA2, ABCA3 normally modulate and stabilize the alveolar surfactant tension; when altered, they can induce an increased stress of the endoplasmic reticulum, which finally lead to epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and apoptosis of type 2 alveolar cells. Polymorphisms of MUC5B, a regulatory mucin, are responsible of mucociliary disfunction, with impaired clearance and enhanced mucus production, which predisposes to bacterial overgrowth and infections.