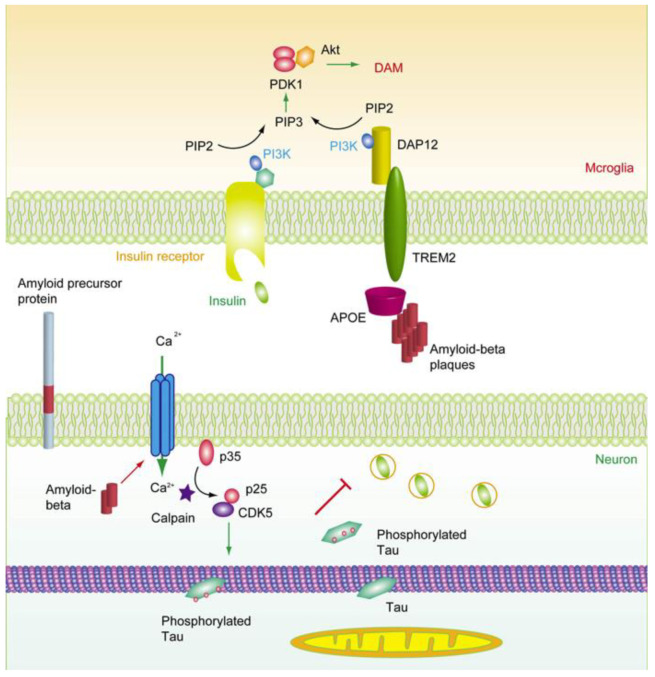
Figure 2.
The deductive role of insulin signaling in AD pathology. Aβ induced calcium influx and the activation of calpain, which further triggered the activation of CDK5 through the cleavage of p35 [31]. CDK5 induced phosphorylation of tau, triggered the detachment of tau from microtubules, and in turn perturbed the function of mitochondria. On the other hand, the microglia switch homeostasis to DAM status in an APOE- and TREM2-dependent manner to protect neurons from the damaging effect of Aβ overproduction [32,33]. TREM2 functions via its adaptor DAP12 (DNAX activation protein of 12 kDa) and PI3K-Akt pathway, which is also regulated by insulin signaling. Thus, insulin can inhibit tau phosphorylation by suppressing GSK3β in neurons and help microglia to maintain the proper DAM status via PI3K-Akt pathway.