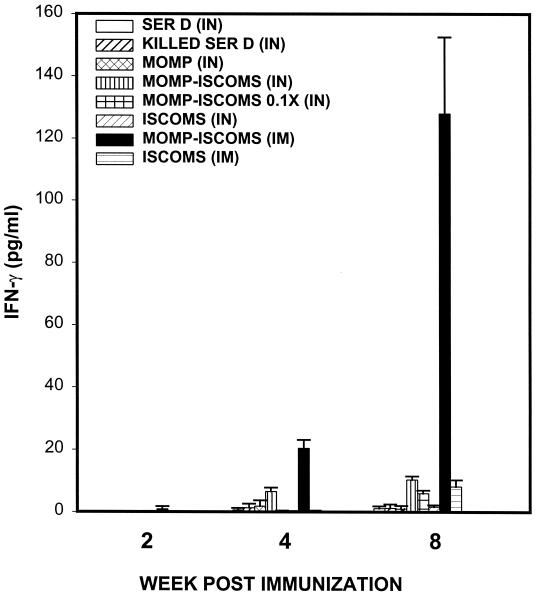
FIG. 1.
Induction of specific genital mucosal Th1 response against C. trachomatis by immunization with MOMP-ISCOMs. Groups of mice (six mice/group) were vaccinated three times every 3 weeks with the indicated regimens, as described in Materials and Methods. The level of Th1 response induced and amount of Th1 recruitment into the genital mucosa were determined by measuring the response of chlamydia-specific, IFN-γ-secreting T cells from genital tract tissues of infected mice, as previously described (24). The antigen used in culture was UV-inactivated EBs (at a multiplicity of infection of 5 EBs:APC) in each stimulated well. The amounts of IFN-γ contained in supernatants derived from culture-stimulated cells and controls were measured by ELISA. The concentration of the cytokine in each sample was obtained by extrapolation from a standard calibration curve generated simultaneously. Data were calculated as the mean values (± SD) of triplicate cultures for each experiment. The control cultures without antigens did not contain detectable levels of the cytokine, and so the data were excluded from the results.