Figure 1.
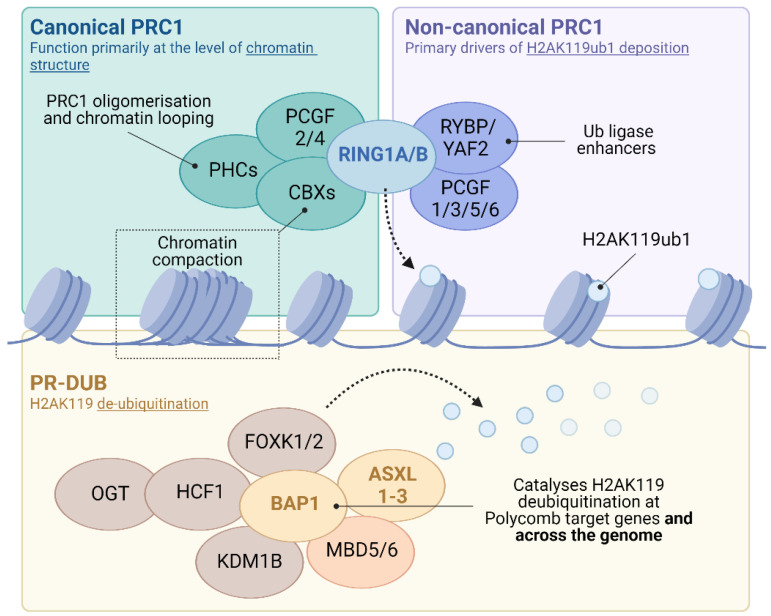
PRC1 complexes contain a highly conserved catalytic core consisting of one of two interchangeable E3 ubiquitin ligases (RING1A or RING1B), which form mutually exclusive heterodimers with one of six Polycomb group RING-finger domain proteins (PCGF1-6). Additional subunits allow the classification of PRC1 into cPRC1 and ncPRC1 forms. cPRC1 complexes assemble around a dimer of RING1A/B and either PCGF2 or PCGF4. Additional subunits including CBX2, CBX4, CBX6, CBX7 or CBX8 and PHC1, PHC2 or PHC3 proteins. CBX proteins have an affinity for histone H3 lysine methylation (e.g. H3K27me3) and are important for PRC1 targeting to chromatin alongside roles in chromatin compaction. In addition, the presence of PHC proteins enable cPRC1 to modulate higher order chromatin structure. In contrast, ncPRC1 complexes comprise dimers of RING1A/B and PCGF1, 3, 5 or 6 associated with either RING and YY1 Binding Protein (RYBP) or its homolog YY1 Associated Factor 2 (YAF2) in place of CBX. The inclusion of RYBP or YAF2 in ncPRC1 greatly enhances RING1A/B catalytic activity, such that ncPRC1s contribute to the majority of H2AK119ub1 in vivo. PR-DUB complexes contain a catalytic core of BAP1, which forms mutually exclusive complexes with one of three additional sex combs-like paralogues (ASXL1-3). PR-DUB complexes function in the cleavage of ubiquitin conjugates from both chromatin and soluble protein targets, including H2AK119ub1. Additional subunit interactions modulate PR-DUB targeting and function, including the transcription factors FOXK1/2, chromatin modifiers OGT and KDM1B, transcriptional cofactor HCF-1 and members of methyl-CpG-binding family MBD5 and 6.