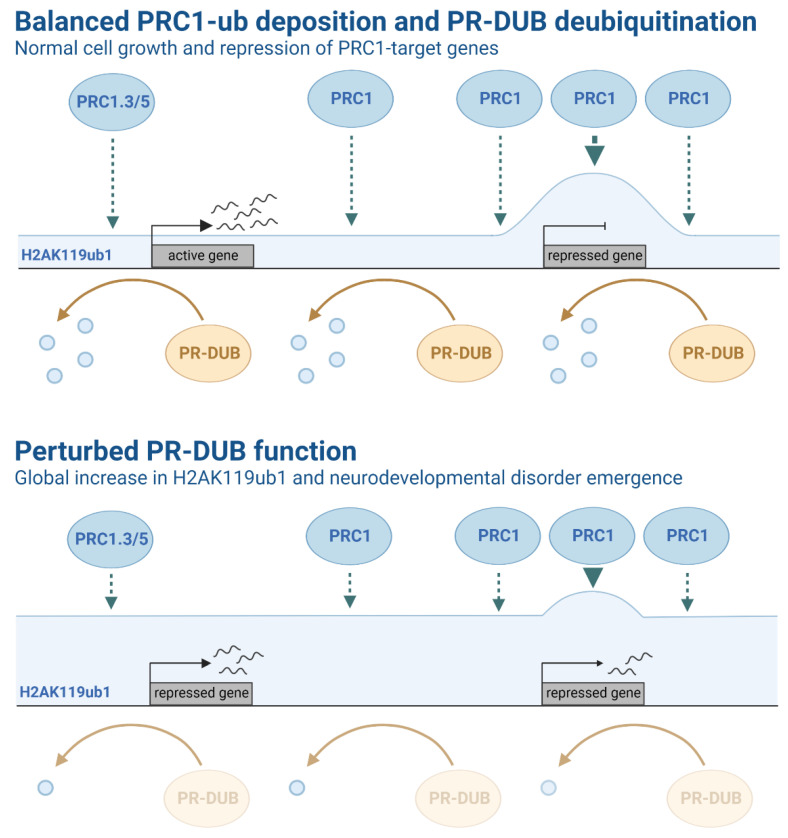
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of Polycomb group (PcG) complex activity and related histone ubiquitination levels. Top: Active (PRC1-low, H2AK119ub1-low) and repressed (PRC1-high, H2AK119ub1-high) gene promoter regions are represented in the context of balanced PRC1-ub deposition and PR-DUB deubiquitination function. PRC1 is highly localised to target gene promoter regions, ultimately resulting in enriched levels of H2AK119ub1 and the repression of key PcG target genes. PR-DUB regulates H2A ubiquitination, which may function to maintain balanced H2A ubiquitination levels across the genome, counteracting PRC1-mediated H2A ubiquitination and leading to transcription. Bottom: Mutations in several components that modulate H2A ubiquitination have been associated with several syndromes and brain pathologies. For example, germline mutations of ASXL1-3 subunits in PR-DUB have been identified in patients with rare congenital disorders. Notably, patients with Bainbridge-Ropers syndrome have been shown to exhibit higher levels of H2A ubiquitination and differential gene expression, suggesting disruption of PR-DUB function. Two promoter regions (first: PRC1-low, H2AK119ub1-high; second PRC1-high, H2AK119ub1-high) genes are represented in the context of perturbed PR-DUB function. Reduced PR-DUB deubiquitination function results in a global increase of H2AK119ub1 at target genes.