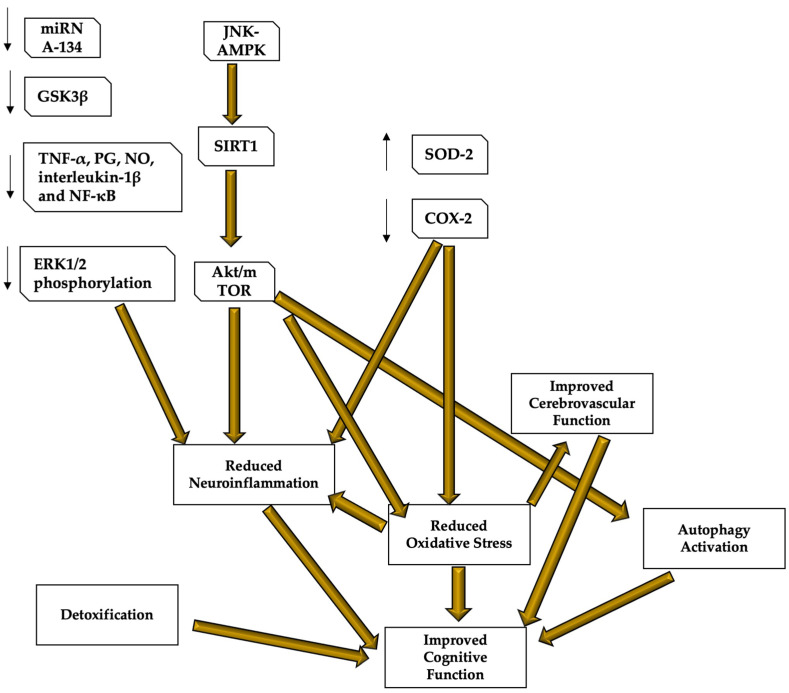
Figure 3.
Resveratrol and hydroxytyrosol molecular mechanisms of action. Resveratrol and hydroxytyrosol demonstrated to be able to improve cognitive performance and protect the brain from neurodegenerative and age-related diseases, mostly thanks to their role in regulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, cerebral blood flow, and autophagy, as well as because of their capacity of detoxifying the blood from those neuro-damaging compounds. Most of the mechanisms are still under study, but it seems that both resveratrol and hydroxytyrosol target the AMPK and the subsequent pathway leading to SIRT1 and Akt/mTOR to reduce neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, and stimulating autophagy. Oxidative stress reduction also inhibits inflammatory responses and stimulates cerebrovascular function, leading to better cerebral blood flow and brain functioning. These compounds are also important detoxicants. Resveratrol mechanisms are clearer and its role in reducing neuroinflammation has been also related to the capacity of lowering mRNA134, GSK3β, ERK1/2 phosphorylation and cerebral levels of TNF-α, PG, NO, interleukin-1β and NF-κB. Resveratrol also increases SOD-2 protecting functions and inhibits COX-2 to reduce ROS production. AMPK—AMP-activated protein kinase; COX—cyclooxygenase; ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase; LPS—lipopolysaccharide; MMP9—matrix metalloproteinase 9; NF-κB—nuclear factor κB; NO—nitric oxide, PGES-1—prostaglandin E synthase-1; ROS—reactive oxygen species; TNF—tumor necrosis factor; SOD—superoxide dismutase. Images have been created by using the functionalities of Microsoft PowerPoint 365 Version 2112. https://www.microsoft.com/microsoft-365 (accessed on 30 November 2022). Used with permission from Microsoft.