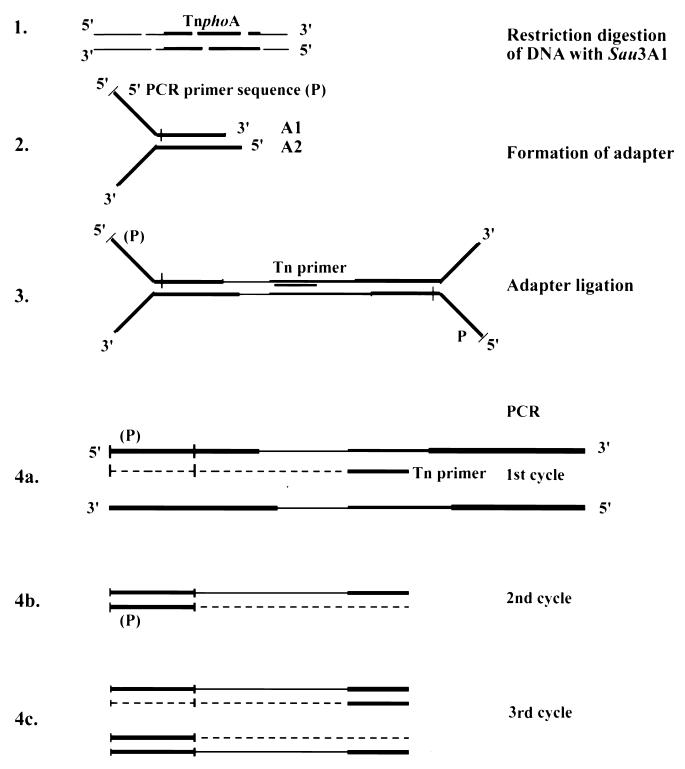
FIG. 1.
Schematic of the Y-adapter PCR. In step 1, chromosomal DNAs of the TnphoA insertion containing strains are digested with restriction enzyme Sau3A1. In step 2, a Y-adapter linker (the Y region is noncomplementary) is prepared from oligonucleotides A1 and A2. In step 3, the Y-adapter is ligated to the restriction fragments. In step 4, the adapter-ligated DNAs are used as templates for PCRs with a Y-adapter (indicated as the 5′ PCR primer [P]) and a transposon-specific primer. Since the 5′ primer sequence is from the same strand as the Y region, it requires a first round of PCR with the Tn primer (step 4a). The resulting single-stranded DNA serves as the template for annealing of the “P primer” in the second round of PCR (step 4b). The resulting PCR products from subsequent cycles are cloned and sequenced to identify the transposon junction.