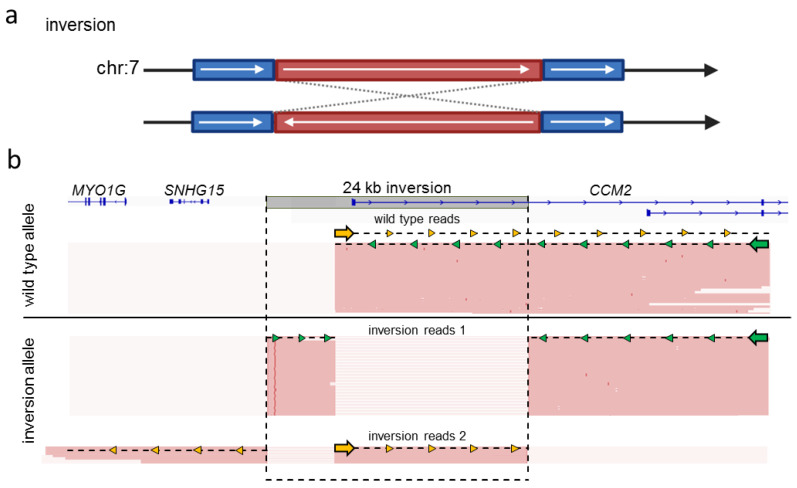
Figure 4.
Nanopore sequencing confidently detected a 24 kb inversion in CCM2. (a) Schematic representation of the inversion in CCM2. (b) A dual-cut approach was used to re-sequence a sample with a known heterozygous 24 kb inversion in CCM2. CrRNAs facilitated sequencing in opposing directions. One binding site was located inside of the inversion (yellow arrow), and the other one was located downstream of the variant (green arrow). Sequencing of the wild-type allele resulted in one type of reads localized between both crRNA cut sides. Two distinct read patterns visualizing the inversion could be observed depending on which crRNA initiated sequencing of the inversion allele (inversion reads 1; inversion reads 2). Read data were inspected in IGV [23]. The Locus Reference Genomic (LRG) transcripts are shown (b).