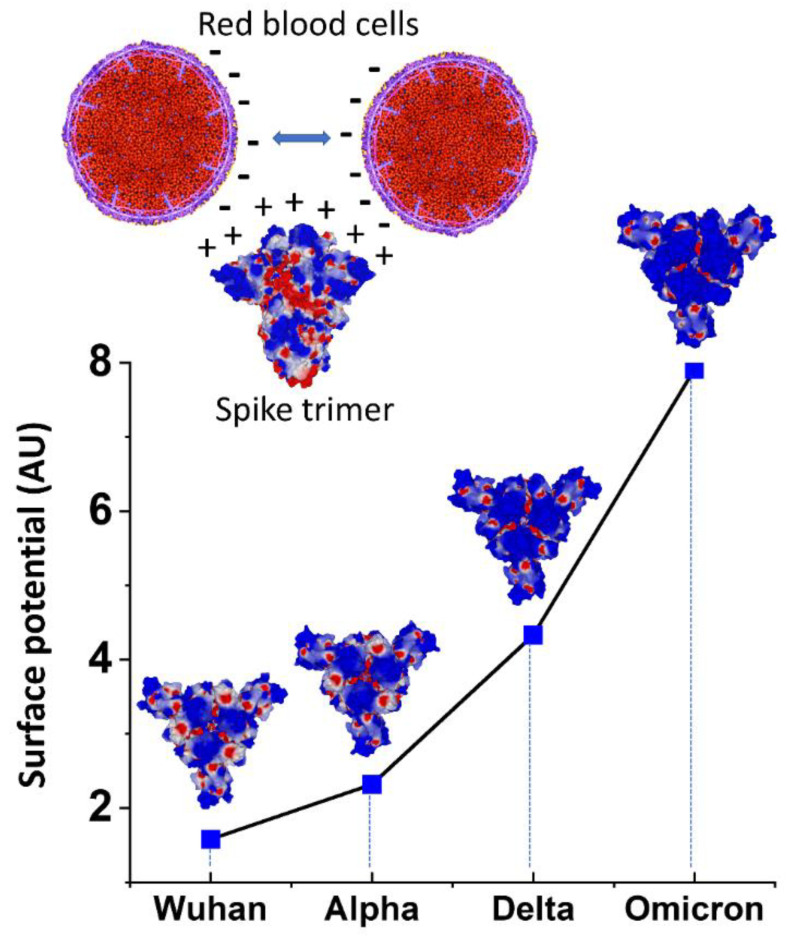
Figure 5.
Electrostatic surface potential of SARS-CoV-2 spike trimers as denoted by color, positive in blue and negative in red. Upper panel. Under physiological conditions, RBCs maintain separation from each other due to a repulsive electric zeta potential between their negatively charged surfaces. The electropositive surface of spike protein neutralizes this zeta potential, allowing closer contacts between RBCs. Lower panel. For all variants, the electrostatic surface potential of the spike trimer is more electropositive in the central area formed by the RBD of each monomer. Quantitative analysis of the surface potential (in AU = arbitrary units) shows an exponential increase from the Wuhan to Omicron lineages.