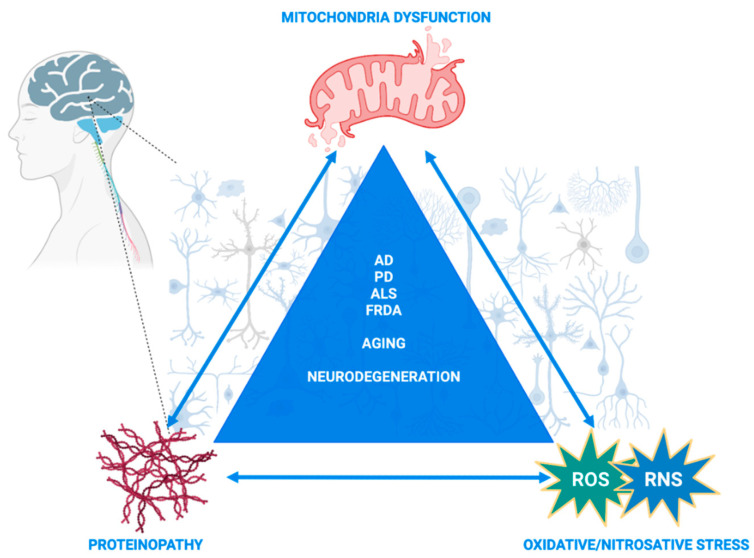
Figure 8.
Trigonal interaction of ROS/RNS, mitochondria dysfunction and proteinopathy in aging and neurodegenerative disorders. In AD, PD, ALS and FRDA, mitochondria dysfunction is accompanied by increased oxidative/nitrosative stress, which in turn can trigger protein misfolding. Toxic protein aggregates such as Aβ, tau, a-synuclein and SOD1 can impair mitochondria homeostasis and further trigger ROS/RNS. Frataxin deficiency leads to mitochondria dysfunction and increased NO production, while the NO-mediated S-nitrosylation of iron-regulating proteins further increases iron accumulation and ROS/RNS production. Hallmark genes in AD, PD and ALS can be mutated and their effects on mitochondria homeostasis are phenocopied by redox modifications of the wild-type proteins. Created with BioRender.com.