Figure 7: In vivo treatment with GC4419 protects aged C57BL6/J mice from agonist induced generation of ROS, phosphatidylserine exposure, and arterial thrombosis.
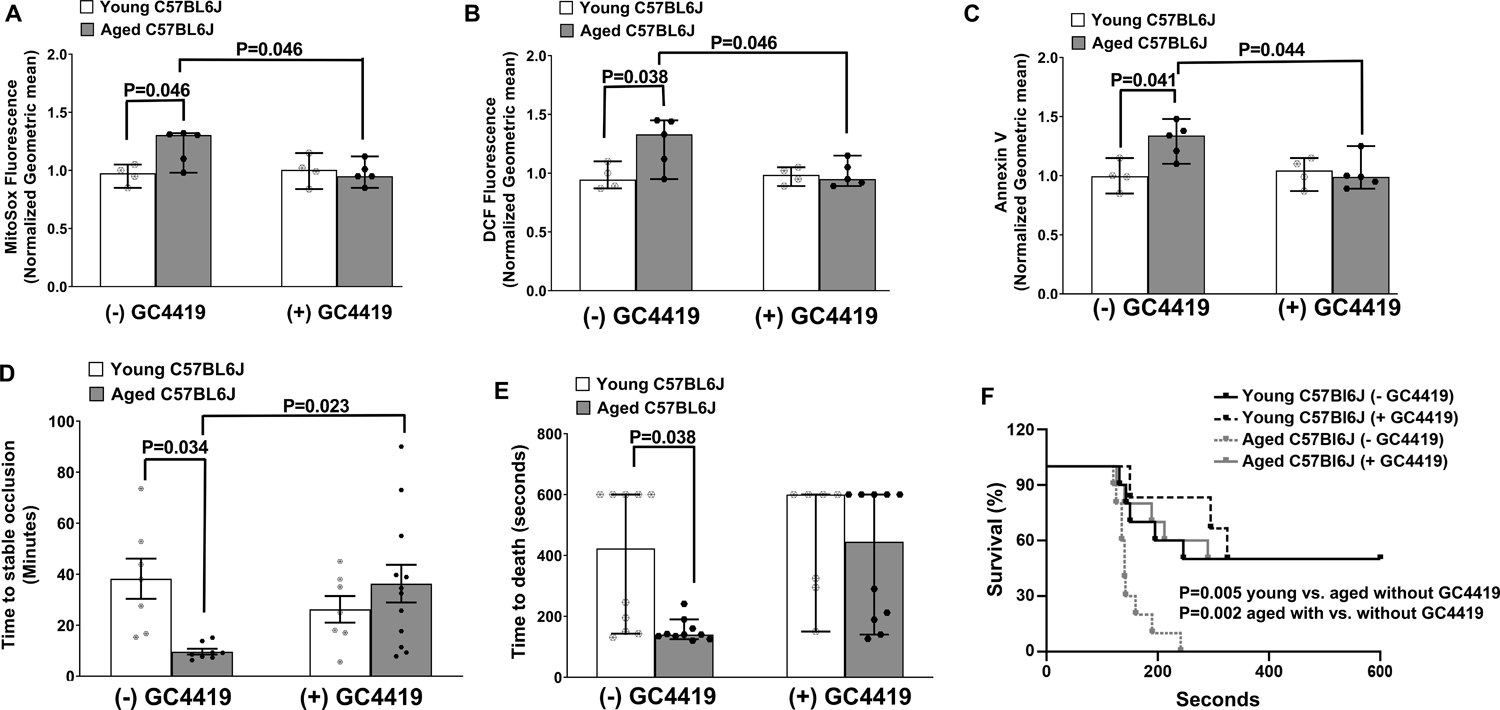
Young or aged C57BL6/J mice were treated with (+) GC4419 (10 mg/Kg daily, IP) or vehicle buffer (− GC4419) for 2 weeks. Washed platelets were prepared and activated with 0.1 U/mL thrombin and 100 ng/mL convulxin and analyzed via FACS. A. Mitochondrial pro-oxidants detection using MitoSox. B. Levels of intracellular ROS detected by oxidation of CM-H2DCF (DCF Fluorescence). C. Annexin V binding. The fluorescent signals for A-C were normalized to respective young control mice receiving vehicle buffer. D. Time to stable occlusion of the carotid artery following photochemical injury. E. Time to death after infusion with 0.5 μg/g collagen. F. Survival curve of E. Data for A-C and E are presented as median with 95% CI and analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test for multiple group comparisons. Data for D are presented as mean ± SE and analyzed using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s analysis for multiple group comparisons. Data for F is analyzed using Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. N = 4–12 per group.
