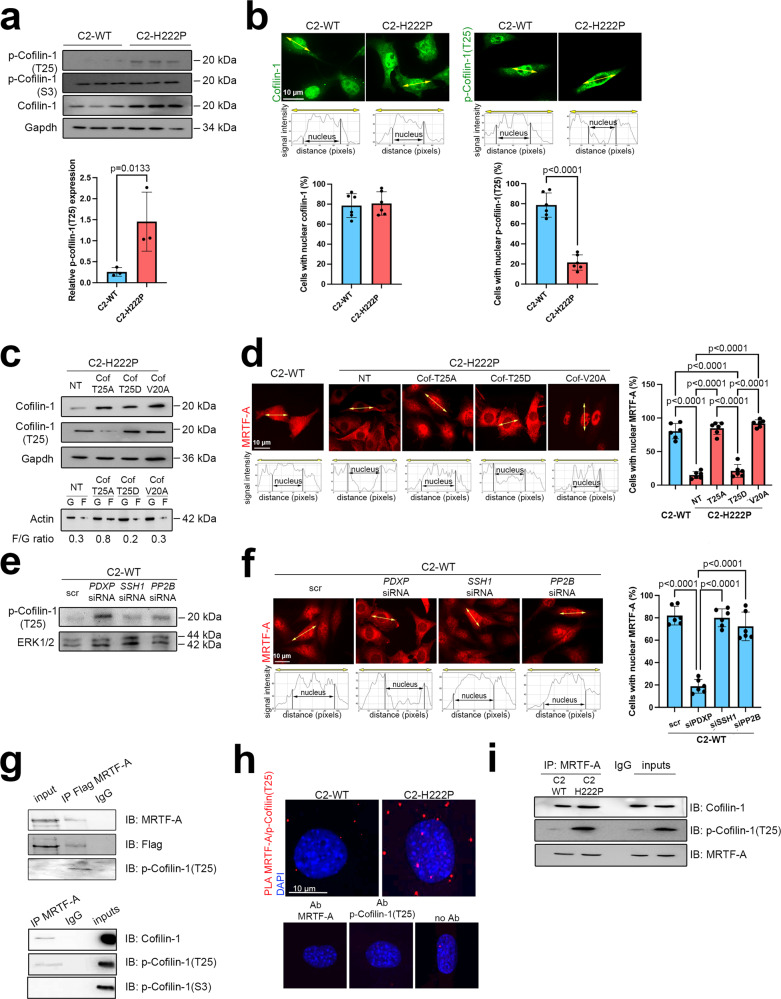
Fig. 2. Cofilin-1 phosphorylated on threonine 25 binds to MRTF-A and prevents its nuclear localization.
a Immunoblots showing total, phospho(S3) and phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 expression in C2-WT and C2-H222P cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Bar graph shows the quantification of phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 (n = 3 independent experiments, mean ± SD). b Representative immunofluorescence staining of cofilin-1 and phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 in C2-WT and C2-H222P cells. Scan line graphs represent the intensity of staining along the yellow arrows. Bar graph shows quantification of nuclear cofilin-1 (n = 487 cells, mean ± SD) and phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 staining (n = 472 cells, mean ± SD). c Immunoblots showing cofilin-1 and monomeric G-actin (G) vs. filamentous F-actin (F) expression in C2-H222P cells transfected with plasmids expressing nonphosphorylatable (T25A), phosphomimetic (T25D), and NES-mutated (V20A) forms of cofilin-1. GAPDH was used as a loading control. F/G ratios were calculated from n = 3. d Representative immunofluorescence staining and scan lines of MRTF-A in C2-WT and C2-H222P cells transfected with same plasmids as in (c). Bar graph shows the quantification of nuclear MRTF-A (n > 200 cells over 6 independent experiments, mean ± SD). e Immunoblots showing phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 expression in C2-WT cells transfected with siRNAs silencing PDXP, SSH1 or PP2B phosphatases. ERK1/2 was used as a loading control. f Representative immunofluorescence staining and scan lines of MRTF-A in C2-WT cells transfected with the same siRNAs as in (e). Bar graph shows the quantification of nuclear MRTF-A (n > 200 cells over six independent experiments, mean ± SD). g Immunoblots showing the interaction of phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 and MRTF-A. Top: proteins from C2C12 were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibody and immunoblotted with MRTF-A or phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 antibodies. Bottom: proteins from C2C12 were immunoprecipitated with MRTF-A antibody and immunnoblotted with cofilin-1, phospho(T25)-cofilin-1, or phospho(S3)-cofilin-1 antibodies. IgG was used as a negative control. h Representative micrographs from proximity ligation assay (PLA) between MRTF-A and phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 in C2-WT and C2-H222P cells. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. No positive PLA reactions (red dots) were observed for MRTF-A or phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 alone or for negative control without primary antibodies (no Ab). i Immunoblots showing the interaction of phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 and MRTF-A. Proteins from C2-WT (n = 3) and C2-H222P (n = 3) cells were immunoprecipitated with MRTF-A and immunoblotted with cofilin-1 or phospho(T25)-cofilin-1 antibodies. IgG was used as a negative control. For g–i representative of three independent repeats is shown. Statistics: for a and b, unpaired two-tailed t-test; for d and f, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.