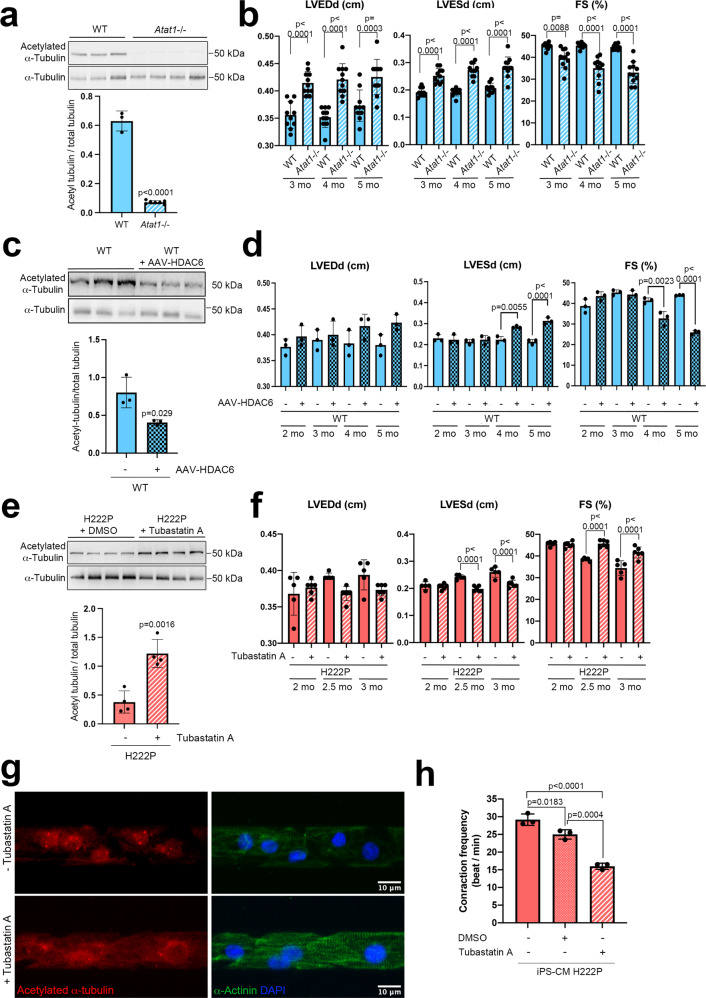
Fig. 5. α-Tubulin acetylation mediates cardiac function in Atat1 knock-out mice and in mice expressing cardiomyopathy-causing mutant A-type lamins.
a, c, e Top: Immunoblots showing the cardiac protein expression of acetylated and total α-tubulin a in 6-month-old male Atat1+/+ (WT) mice (n = 3) and Atat1 knockout mice (Atat1−/−) (n = 5) c in 5-month-old male WT mice (n = 3) and WT mice transduced with AAV expressing HDAC6 (n = 3), and c in 3-month-old male Lmnap.H222P/H222P (H222P) mice treated with tubastatin A for one month (n = 4) compared with mice treated with DMSO (n = 4). a, c, e Bottom: bar graph showing the quantification of acetylated α-tubulin normalized to total α-tubulin (mean ± SD). b, d, f Bar graphs showing the left ventricular end-diastolic diameters (LVEDd), end-systolic diameters (LVESd) and fraction shortening (FS) (mean ± SEM) b in Atat1+/+ (WT) mice (n = 10) and Atat1 knockout mice (Atat1−/−) (n = 11) from 3 to 6 months of age, d in 5-month-old male WT mice (n = 3) and WT mice transduced with AAV expressing HDAC6 (n = 3) and f in 3-month-old male Lmnap.H222P/H222P (H222P) mice treated for one month with tubastatin A (n = 6) compared to mice treated with DMSO (n = 5). g Immunofluorescence staining of acetylated α-tubulin and α-actinin in cardiomyocytes derived from iPS cells from a patient carrying the LMNA p.H222P mutation, 40 days post-differentiation, treated (lower panel) or not (upper panel) with 3 µM of tubastatin A for 24 h. α-Actinin is shown as cardiomyocyte differentiation marker. h Contraction frequency of cardiomyocytes derived from iPS cells from a patient carrying the LMNA p.H222P mutation, 40 days post-differentiation, treated or not with 3 µM of tubastatin A for 24 h (n = 3 technical replicates) (mean ± SD). Statistics: for a, c, e unpaired two-tailed t-test; for b, d, f, h one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.