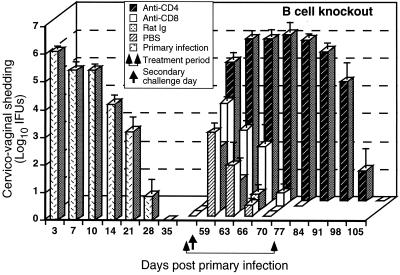
FIG. 2.
Effect of anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 treatment on the resolution of a secondary C. trachomatis genital tract infection of B-cell-deficient mice. Mice were infected vaginally with 100 ID50 of C. trachomatis, and the course of the primary infection was monitored. Following resolution of the primary infection, immune mice were divided into four groups of five mice each and treated with either anti-CD4, anti-CD8, rat Ig, or PBS as described in Materials and Methods. Treated mice were challenged vaginally with 100 ID50 of C. trachomatis on day 56, and the infection was monitored by swabbing the vaginal vault and enumerating IFU on HeLa cell monolayers. Data are presented as log10 IFU and represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean of triplicate determinations of five mice. P < 0.05 for anti-CD8-, rat Ig-, and PBS-treated mice compared to primary infection of mice at days 3, 7, 10, 14, and 21 days post infectious challenge. P < 0.05 for anti-CD4-treated mice compared to primary infection of mice at days 3, 14, 21, 28, 35, and 42 post infectious challenge.