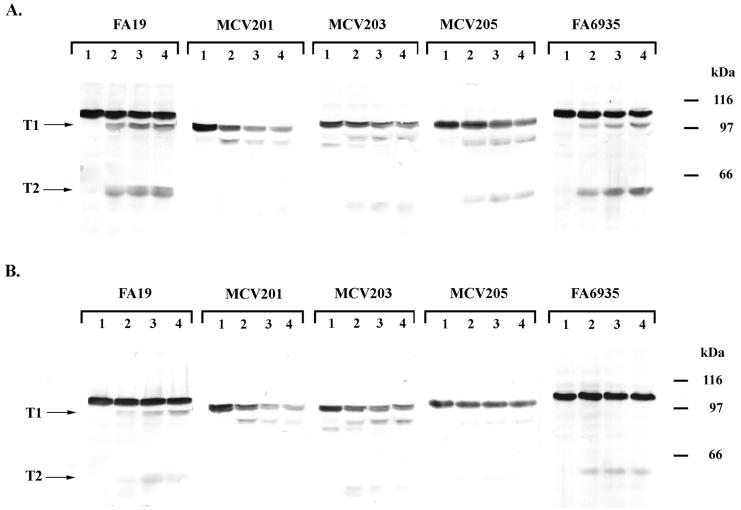
FIG. 6.
Trypsin accessibility of mutant TbpAs in the presence and absence of ligand. (A) Whole, iron-stressed cells from the indicated gonococcal strains were treated with trypsin (0.5 μg/ml) for 0 min (lane 1), 10 min (lane 2), 20 min (lane 3), or 30 min (lane 4) as indicated above each panel. Whole-cell lysates were prepared from the trypsinized cells, and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. The resulting Western blots were probed with polyclonal anti-TbpA serum (16). (B) Whole, iron-stressed cells from the indicated gonococcal strains were exposed to 100 nM iron-saturated Tf and then treated with trypsin (0.5 μg/ml) for 0 min (lane 1), 10 min (lane 2), 20 min (lane 3), or 30 min (lane 4) as indicated above each panel. The resulting Western blots were probed with polyclonal anti-TbpA serum (16). The labels T1 and T2 on the left of each panel indicate the positions of two characteristic products that resulted from limited proteolysis of TbpA. Approximate positions of molecular mass standards are indicated in kilodaltons on the right of each panel. Images were scanned using a Hewlett-Packard ScanJet 6300c. The final images were annotated using Adobe Photoshop 4.0.