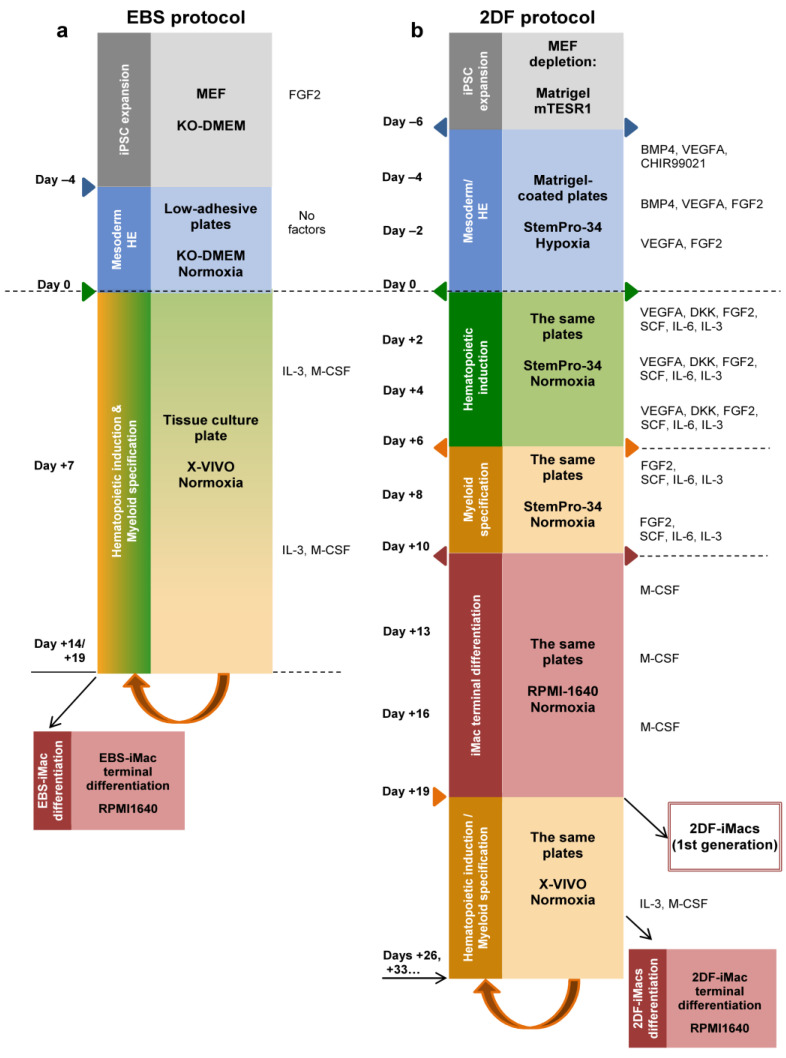
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of iMac differentiation procedures using embryoid-body-dependent spontaneous (EBS) and embryoid-body-independent exogenous factor-dependent (2DF) differentiation protocols. (a) EBS protocol. induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were expanded on mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells (MEFs) and collected and cultured in low-adherent conditions in the absence of exogenous differentiation factors (day −4 to day 0) to induce embryoid body (EB) formation. At day 0, EBs were collected and transferred to culture tissue plates, where they were cultured in the presence of IL-3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) to induce hematopoietic specification and myeloid differentiation. When floating iMac precursors appeared in the culture (day +14 to day +19), they were collected and differentiated into EBS-iMacs in the presence of M-CSF. The remaining cultures were restimulated with IL-3/M-CSF to continue the generation of EBS-iMac precursors followed by their terminal differentiation into EBS-iMacs. (b) The 2DF protocol. To induce mesoderm/HE, MEF-depleted iPSCs were cultured in tissue culture plates coated with Matrigel in the presence of indicated exogenous factors (day −6 to day 0). On day 0, the composition of exogenous factors was changed in a way to induce first hematopoietic specification (day 0 to day +6) and next myeloid differentiation (day +6 to day +10). BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; DKK, Dickkopf-related protein 1; FGF2, basic fibroblast growth factor; Flt3L, Fms-related receptor tyrosine kinase 3 ligand; SCF, stem cell factor; TPO, thrombopoietin; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A.