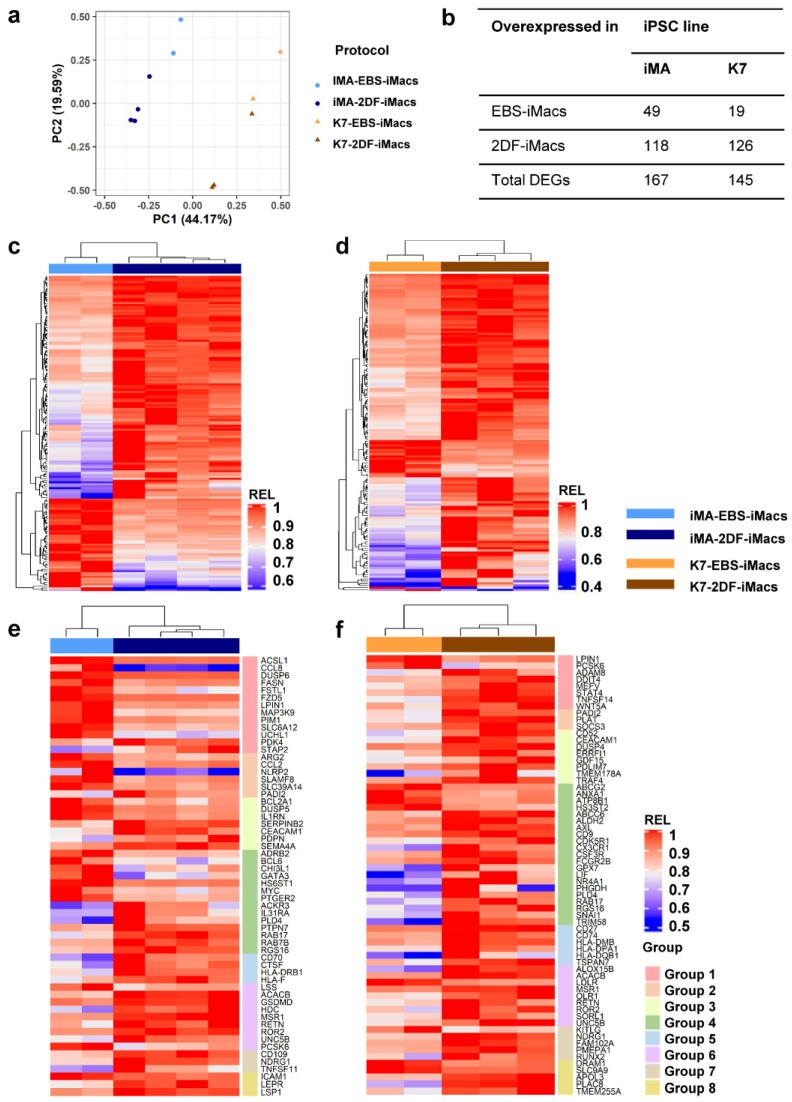
Figure 5.
EBS- and 2DF-iMacs differ by fine transcriptomic characteristics. EBS- and 2DF-iMacs were differentiated in parallel in 4 (iMA) and 3 (K7) independent differentiation experiments. RNA was isolated from the resulting CD14+ sorted iMacs (provided they were formed on time) and sequenced (two batches of iMA-EBS-iMacs and one batch of K7-EBS-iMacs were generated late and were excluded from the analysis). (a) Principal component (PC) analysis showing the separation of iMacs based on the source iPSC line (PC1) and the type of differentiation protocol (PC2). (b) Numbers of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between iMA- and K7-derived EBS-iMacs and 2DF-iMacs. (c,d) Heatmaps depicting the expression of DEGs in iMA- (c) and K7- (d) derived EBS-iMacs and 2DF-iMacs. Expression levels were normalized on the maximal value separately for (i) each gene and (ii) EBS and 2DF differentiation experiments. (e,f) Heatmaps depicting the expression of selected DEGs between EBS- and 2DF-iMacs. (e) iMA-derived iMacs; (f) K7-derived iMacs. DEGs were categorized into 8 functional groups based on gene role in macrophage functionality taken from available published sources. Group 1, genes induced by M1/inflammatory stimuli and involved in pro-inflammatory response; group 2, genes induced by M1/inflammatory stimuli for which both pro- and anti-inflammatory effects have been reported; group 3, genes induced by M1/inflammatory stimuli and involved in the negative regulation of inflammation; group 4, genes associated with M2/TAM macrophages and anti-inflammatory activity; group 5, genes implicated in antigen presentation, endosome functioning and costimulation; group 6, genes involved in lipid homeostasis and foam macrophage formation; group 7, genes implicated in osteoclastogenesis; group 8, genes implicated in phagocytosis and antibacterial response. For detailed description of genes, see Tables S2.1–S2.3.