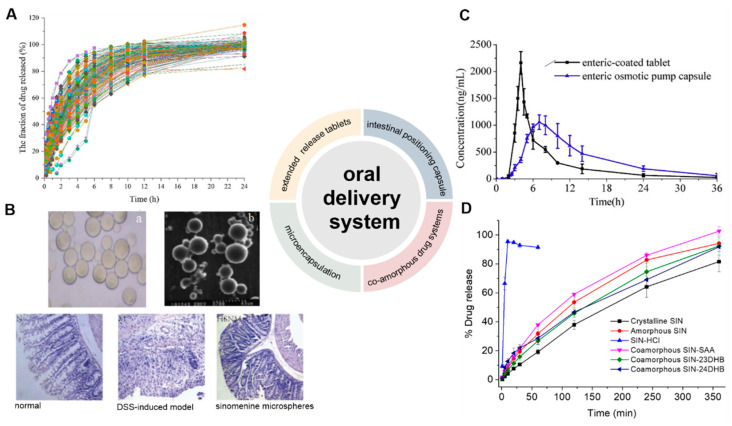
Figure 2.
Development of oral administration systems of SIN. (A) Dissolution profiles of 36 batches of SIN-HCl sustained-release tablets showing complete drug release with a zero-order kinetics (n = 5) [30]. The tablets consisted of with SIN-HCl, osmotic agents, and polymers for promoting permeation. (B) Light (a) and electron microscope (b) images of SIN microspheres, which exhibited improved treatment for DSS-induced mouse models by Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) staining of colon sections in different treatment groups [10]. (C) Plasma concentration–time curves of SIN from both enteric osmotic pump capsules or enteric-coated tablets in beagle dogs after oral administration (n = 6) [28]. (D) Release profiles of SIN from crystalline SIN, amorphous SIN, SIN-HCl, as well as co-amorphous SIN and three different phenolic acids [37]. (Reprinted with permission form Refs. [10,28,30,37]).