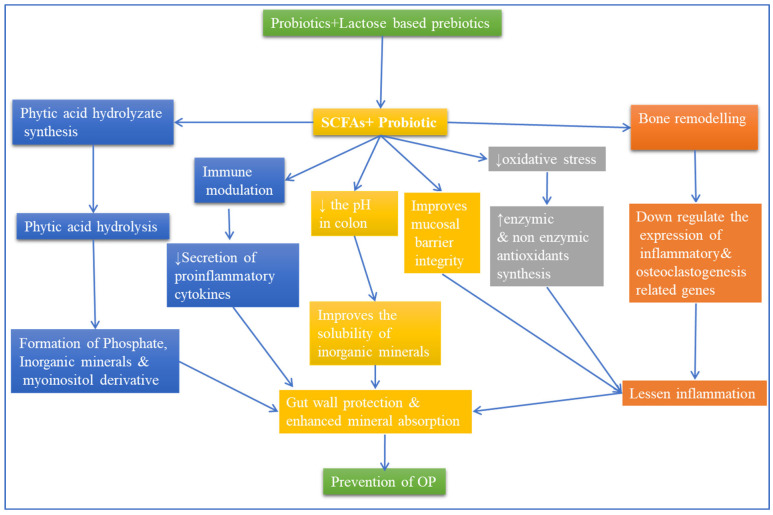
Figure 3.
Effect of microbiota on osteoporosis and the crucial regulatory factors in bone metabolism. Beneficial microbes of the gut are influenced by diet, antibiotics, and probiotics. This impact has downstream ramifications, especially on bone mass, via multiple mechanisms. For instance, microbiota abundance does impact estrogen bioavailability which is crucial in bone mass. Secondly, microbiota does support the immune system by modulating the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Thirdly, gut microbiota can generate metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids. It has also been shown that gut microbiota does alter intestinal permeability and enhances vitamin D availability and bone mineral absorption. Finally, the gut microbiome is known to affect the gut-brain axis via the modulation of the abundance of hormones: 5-HT- 5-hydroxytryptamine; IGF-insulin-like growth factor, SCFA, short-chain fatty acid, PTH-Parathyroid hormone.