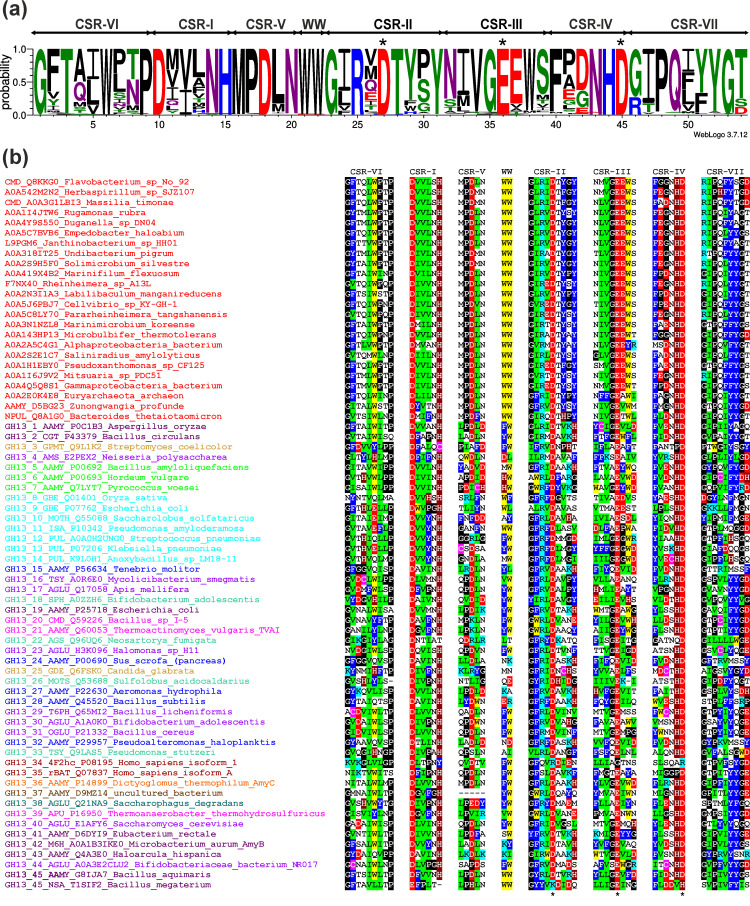
Figure 3.
(a) Sequence logo of the newly proposed GH13 subfamily GH13_46. CSR-I, residues 10–15; CSR-II, residues 23–31; CSR-III, residues 32–39; CSR-IV, residues 40–45; CSR-V, residues 16–20; CSR-VI, residues 1–9; CSR-VII, residues 46–54; WW region, residues 21–22. The catalytic triad, i.e., the catalytic nucleophile (No. 27, aspartic acid), the proton donor (No. 36, glutamic acid), and the transition-state stabilizer (No. 45, aspartic acid) are indicated by asterisks. The logo is based on 108 sequences. (b) Conserved sequence regions for the α-amylase representatives. Twenty-four selected members (of all 108 studied in the logo) of the newly proposed GH13 subfamily represented by the cyclomaltodextrinase from Flavobacterium sp. No. 92 (red sources) and one sequence represented each GH13 subfamily (for details, please, see Table S1). Each protein is labeled by its UniProt accession number and the name of the organism. If known, the enzyme specificity is given preceded by the GH13 subfamily number. The abbreviations of the enzymes are explained in Table S1. The color code for the selected residues: W, yellow; F, Y—blue; V, L, I—green; D, E—red; R, K—cyan; H—brown; C—magenta; G, P—black. The catalytic triad is signified by asterisks below the CSRs.