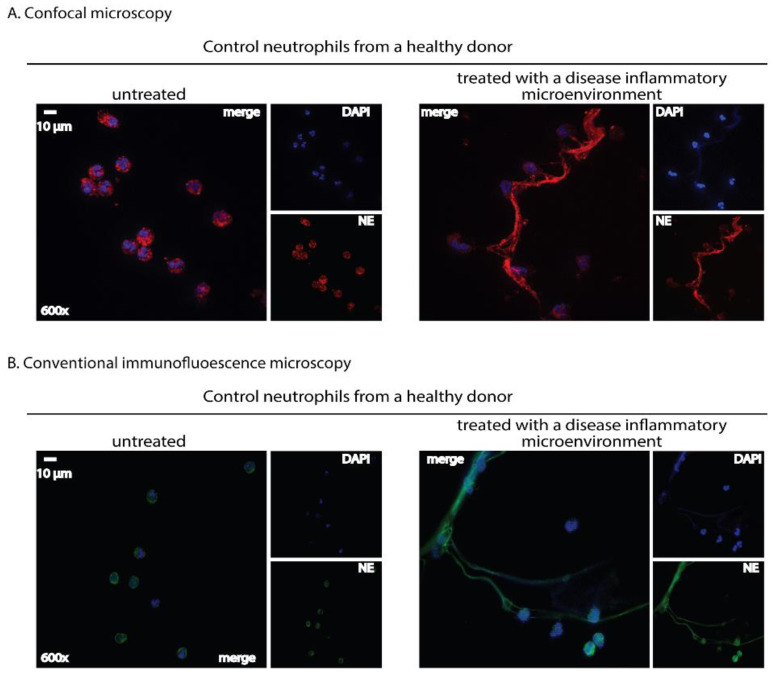
Figure 2.
Immunofluorescence staining: A qualitative tool for NET detection in human-isolated neutrophils using either a confocal or a conventional fluorescence microscope. Neutrophils isolated from healthy donors’ whole blood using a density gradient separation method were stimulated with a serum derived from a treatment-naïve patient with active ulcerative colitis (180 min incubation time). NETs are visualized as fibers of extracellular DNA and neutrophil granule proteins assessed by double-staining with a chromatin-staining dye and a neutrophil marker. (A) Neutrophils were stained with a rabbit anti-human neutrophil elastase ((NE), Abcam, Cambridge, UK) antibody detected by a goat anti-rabbit AlexaFluor 594 antibody (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Visualization was performed using confocal microscopy (Revolution spinning disk confocal system; Andor, Belfast, UK). (B) Neutrophils were stained with a mouse anti-human neutrophil elastase ((NE), Abcam) antibody detected by a goat anti-mouse AlexaFluor 488 antibody (Invitrogen). Visualization was performed using a fluorescence microscope (OLYMPUS BX51, Shinjuku, Japan). In (A,B), cell nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole ((DAPI), Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA). Untreated neutrophils served as control. Data from the Molecular Hematology Laboratory archive are shown.